Diabetes complications
What is diabetes complications ??
High blood sugar level can damage your body part seriously. These effect may shown in diabetics patient is called diabetics complication.
It may divided into two types-
- Acute complications
- Chronic complications
Acute complications
- Hypoglycemic effect- when your blood glucose are too low. It this stage stroke risk are development.
- Hyperglycemia- when your blood glucose are too high. In this stage various chronic complication are development.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis-It is life threatening diabetics complication that developed gradually due to lack of insulin.
Ketoacidosis
Uncontrolled production of ketones bodies like acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetone.
Causes
Lack of insulin body tried to Utilize fat as a fuel source of energy then form excess Ketone bodies .
Symptoms
- Sweating
- Tachycardia
- Palpitation
- Fatigue
- Loss of concentration
- Confusion
- Hunger, headache first
Diagnosis
Confirm in laboratory test
- Glycosuria and Ketone urea
- Glucose, urea, creatine, electrolyte, Venous Bicarbonate would be increase
- Distinct glucose test show 22 mmol/l.
Treatment of ketoacidosis
- Expand fluid volume ( 0.9% sodium chloride)
- Infusion insulin
- Prevent hyperkalemia
What is chronic diabetes complications ?
Chronic diabetes complications is also called long term diabetes complications where it is in serious blood vessel damage of the organ and developed gradually in serious stage. Chronic complication may affect and damage the parts of the body discus bellow.
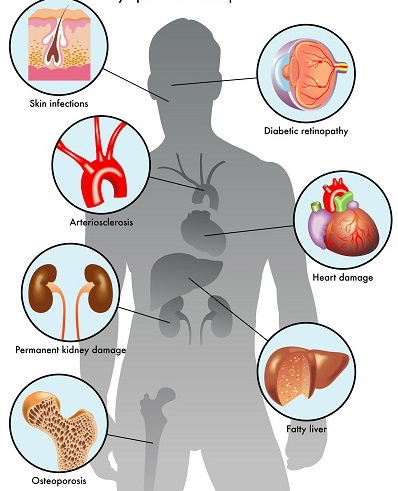
1. Cardiovascular disease
- Myocardial infarction
- Hypertension
- Dyslipidemia
- Atherosclerosis
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Atherosclerosis cramping pain & reversible muscle pain.
2. Retinopathy
Retina is important part for vision of the eye. Retinopathy is characterized by decreasing vision capacity of eye or disease of retina. It is a long term complication of diabetics patients. More then 80% people have had diabetics more then 20 years or longer affected in retinopathy. Two types ratinopathy like non-proliferate due to swelling of the blood vessel around retina and 2nd proliferate due to lacking of oxygen are shown.
Prevent retinopathy-
- Prevent should tight control blood glucose, blood pressure and blood fat.
- Early detected site may be saved by laser photo coagulation in advance case surgery required.
- Pregnancy may worse, moderate to sever retinopathy.
- Don’t smoking
- Treatment may done by using anti vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the retina and corticosteroids.
Nephropathy
Kidney is essential organ of human body. It balance acid base, electrolytes, detoxified toxic elements, filtrate the blood of the body. Kidney disease increase the mortality due to failure its function.
In diabetic renal disease the kidney become
- Enlarged
- Blood pressure increase
- You may diagnosis kidney disease by uric acid test in blood.
- GFR initially increase then decrease and progress reduction of GFR
- GFR diagnosis by albumin creatinine ratio.
protienurea
GRF -Male equal or greater than 2.5 mg per mmol and female 3.5 mmol.
Macroalbuminia
GRF =>30 mg/mmol at end stage 200 mg/mmol.
Protection of kidney
Medication
Should tight control of hyperglycemia and blood pressure. Drug may be treated- ACE inhibitor ( Enalapril) and ARBs ( olmesartan) are preferred by class.
