Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is is a common chronic condition of articular designeration. Secondary changes can occur in bone leading to pain, Decreased functioning and even disability. 55 Yaar elderly people are mostly affected by osteoarthritis disease. Early age from 35 years old and less than 35 also seen affected by this disease. Women are more than three times greater affected by this osteoarthritis than man.
Pathophysiology
-By developing this disease with age the strength of tendons ligaments and muscles declines.
-By apoptosis and inhibiting Proliferation rate number of chondrocytes decline
-Decrease proteoglycans
-Increase interleukin 1 that decrease matrix metalloproteins (MMPs) Proteoglycans
– pain from ( Osteoplytes, synovitis , bursitis ,Tendonitis)
Causes of risk factor
- Female muscle weakness,
- Obesity,
- Joint trauma,
- Heredity
- Congenital or anatomical defects
Clinical presentation
– Deep localized pain in a joint
-Crackling noise heard in the joined upon moving
-Osteoarthritis most commonly affects hips, knees, spine, feet and hands.
Diagnosis
- physical examination
Misshaped join, decrease range of joint motion, joint tenderness
- Laboratory test
for osteoarthritis has no specific laboratory test allow
- Reveal Synovial fluid
- Increase Leukocytosis and mononuclear lymphocytes
- Radiography
– cartilage damage resulting narrowing of joint space
– osteophyte and subchondral sclerosis are seen
Treatment
Treatment goal
– First goal to control pain
-Improve joint mobility
-Minimize functional disability
Pharmacological and Non-pharmacological both treatment are simultaneously important
Non pharmacological treatment
Non pharmacological treatment are most important for the osteoarthritis patient
It may does by
-Patient education ( tips on joint protection and exercise program)
-Weight loss
– Aerobic exercise program to increase muscle strength
– Physical therapy
– Use assistive device
– Acupuncture may reduce the pain
– Thermal therapy
Pharmacological treatment
Pharmacological treatment can divided by two groups ( Mild & Acute osteoarthritis )-
1. For mild pain when initiate osteoarthritis
Medication 1
1.1 . Paracetamol
Dose : 500 mg for 4 times a day not more than 4 g a day
Or
1.2 .1. Non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAID)
Example of this medicine
1.2.1.1. Ibuprofen
Dose: 400 mg 3 times a day not more than 3200 mg per day After meal
Or
- 2.1.2. Diclofenac
It is most effective medicine for NSAIDs group
Dose: 75 mg twice a day not more than 200 mg per day should be taken after meal.
Note: People are mostly hyper gastritis symptoms or peptic ulcer disease or duodenal Ulcer disease or acute renal disease should not use this type of drug in oral form.
This type of medicine inhibit platelet activation resulted inhibit coagulation process. Ulcer patient, haemophilia or any other coagulation disorder patients should not take this medicine.
-
Other analgesic
2.1. Tramadol
Dose: 50 mg 4 to 6 hours interval for 15 days
2.2. Pregabalin
Dose: 25 mg 1 or 2 times a day Initial dose for three to five days Then increase the dose according to tolerance.
2.3. Steroid Anti Inflammatory drugs
Prednisolone
Dose: 5mg 2 times daily for 15 days.
Note : For severe diabetic patients it would be concerned about the use of this medicine. It may increase the blood glucose level.
Prescription –
You can follow some prescription according to your physical condition. All prescription are for adult patient who are more than 16 years old or above.
Prescription N0 1 & 2. for mild osteoarthritis :
Who don’t follow the prescription No. 1,2 & 3 ( Contraindication )-
Patient are suffering by post morbidity or mortality disease like
- Chronic diabetics
- Chronic kidney disease
- Chronic liver cirrhosis
- Peptic or Gastric ulcer patient and any other coagulation disorder patients like hemophilia.
- Heart failure patient
Prescription N0 1 for mild osteoarthritis patient.

Prescription N0 2. :
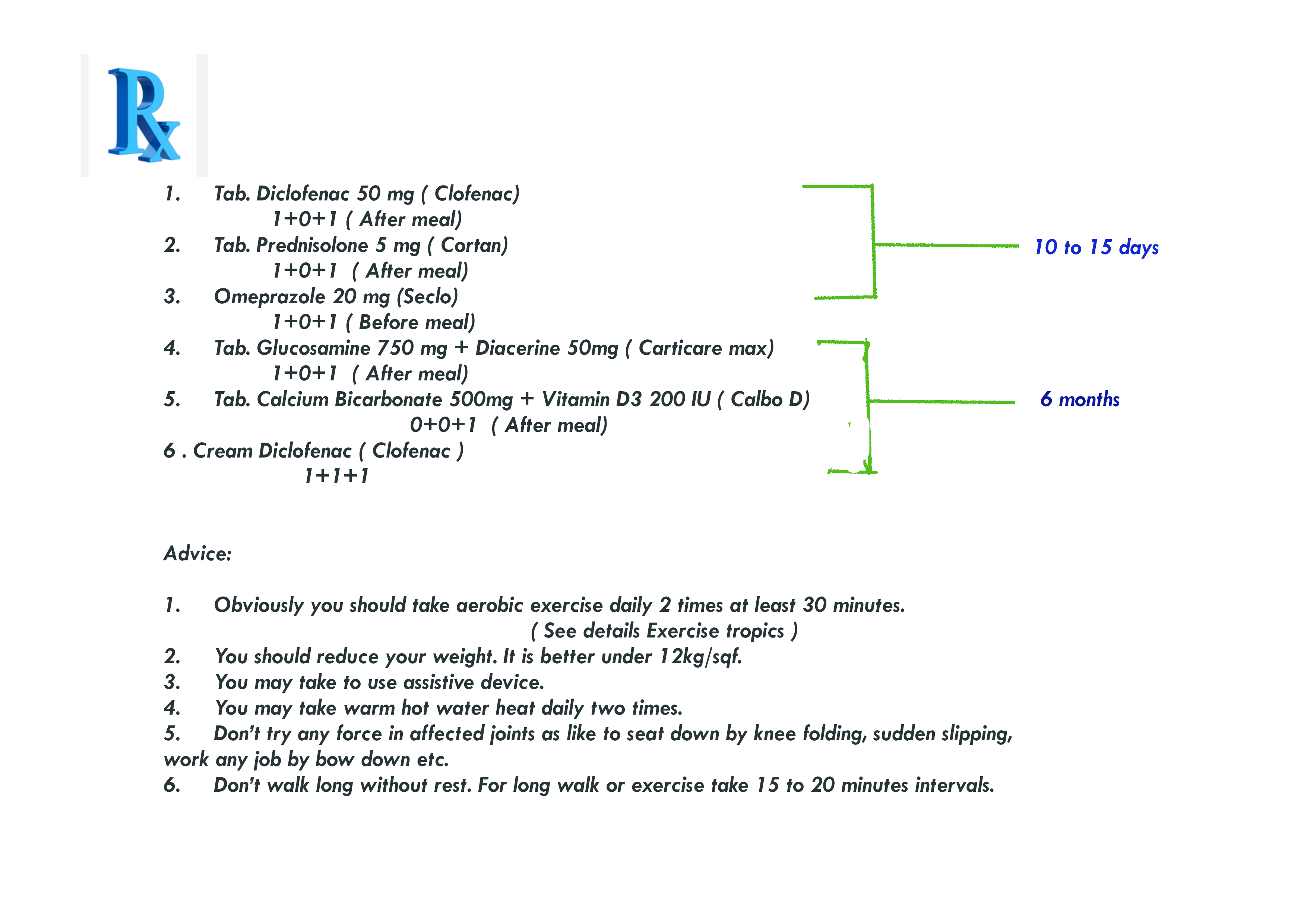
Prescription N0 3. for acute osteoarthritis :
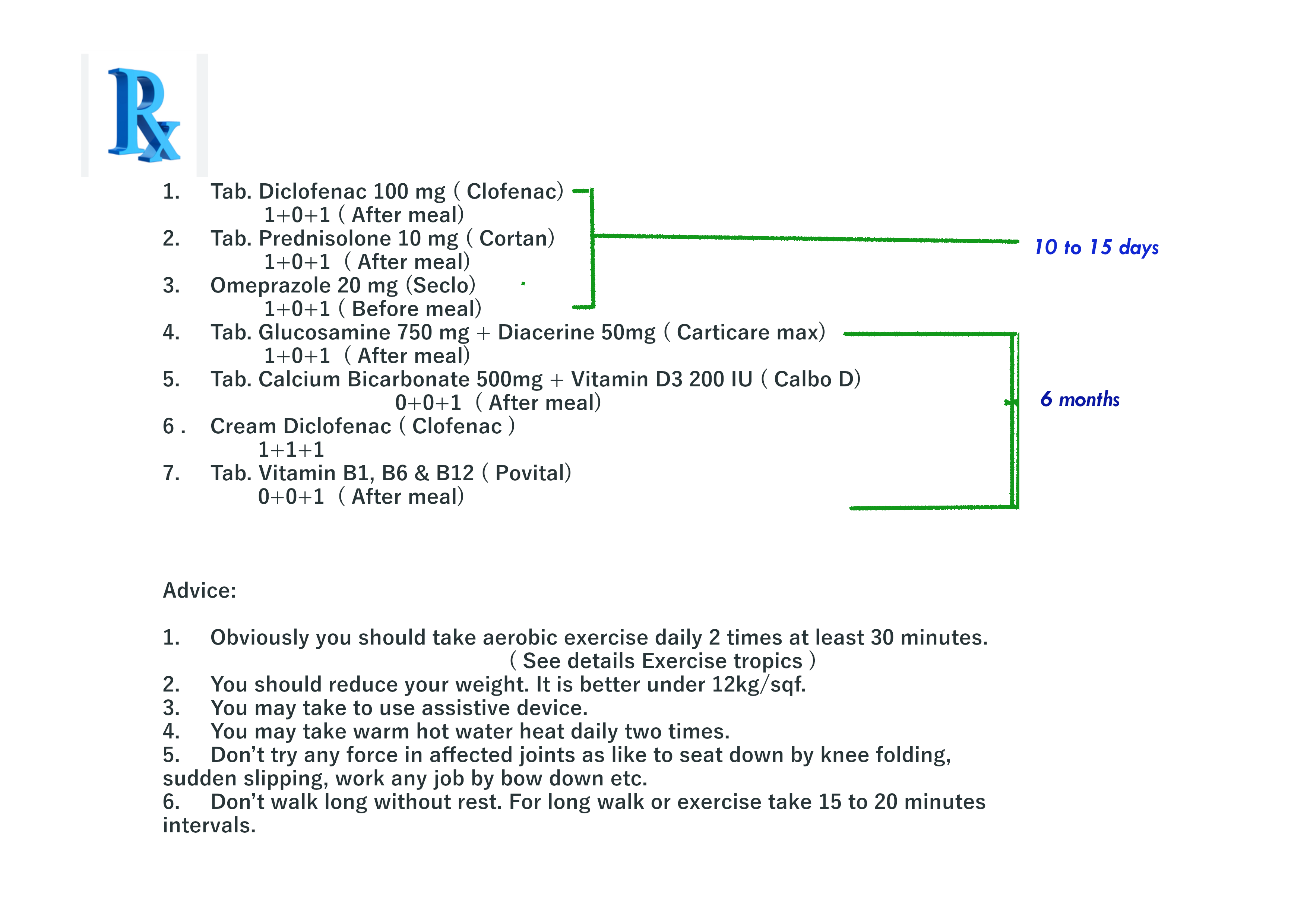
Prescription for osteoarthritis patient who have specific co- morbidity or mortality disease
Prescription No 4. for acute osteoarthritis patient who also a peptic or gastric ulcer patient
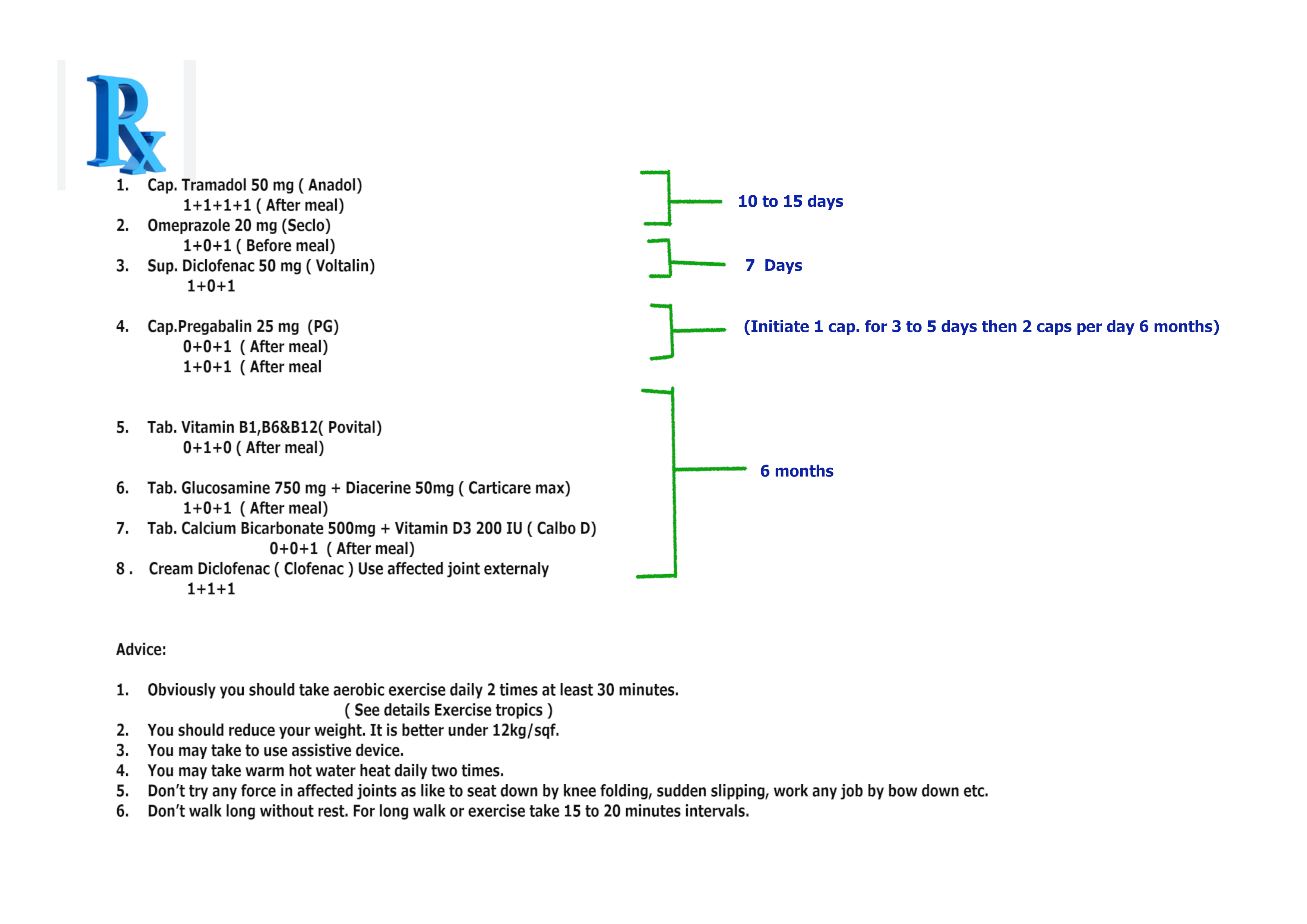
Who don’t follow the prescription No. 4 ( Contraindication )-
Patient are suffering by post morbidity or mortality disease like
- Chronic kidney disease
- Any other coagulation disorder patients like hemophilia.
Prescription No. 5 for mild osteoarthritis patient who have also a mild kidney disease-
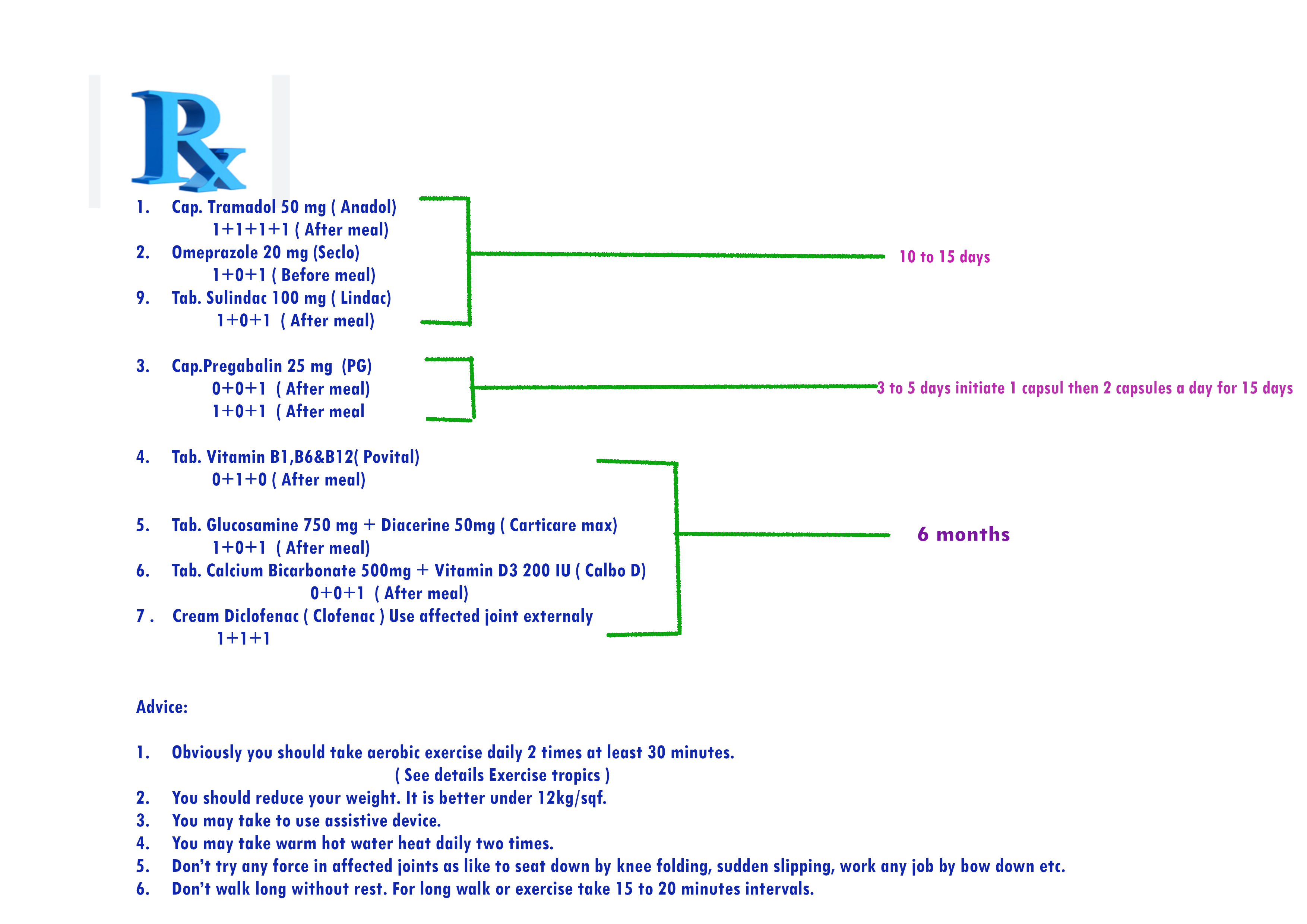
Prescription No.6 for Acute osteoarthritis patient who have mild kidney disease
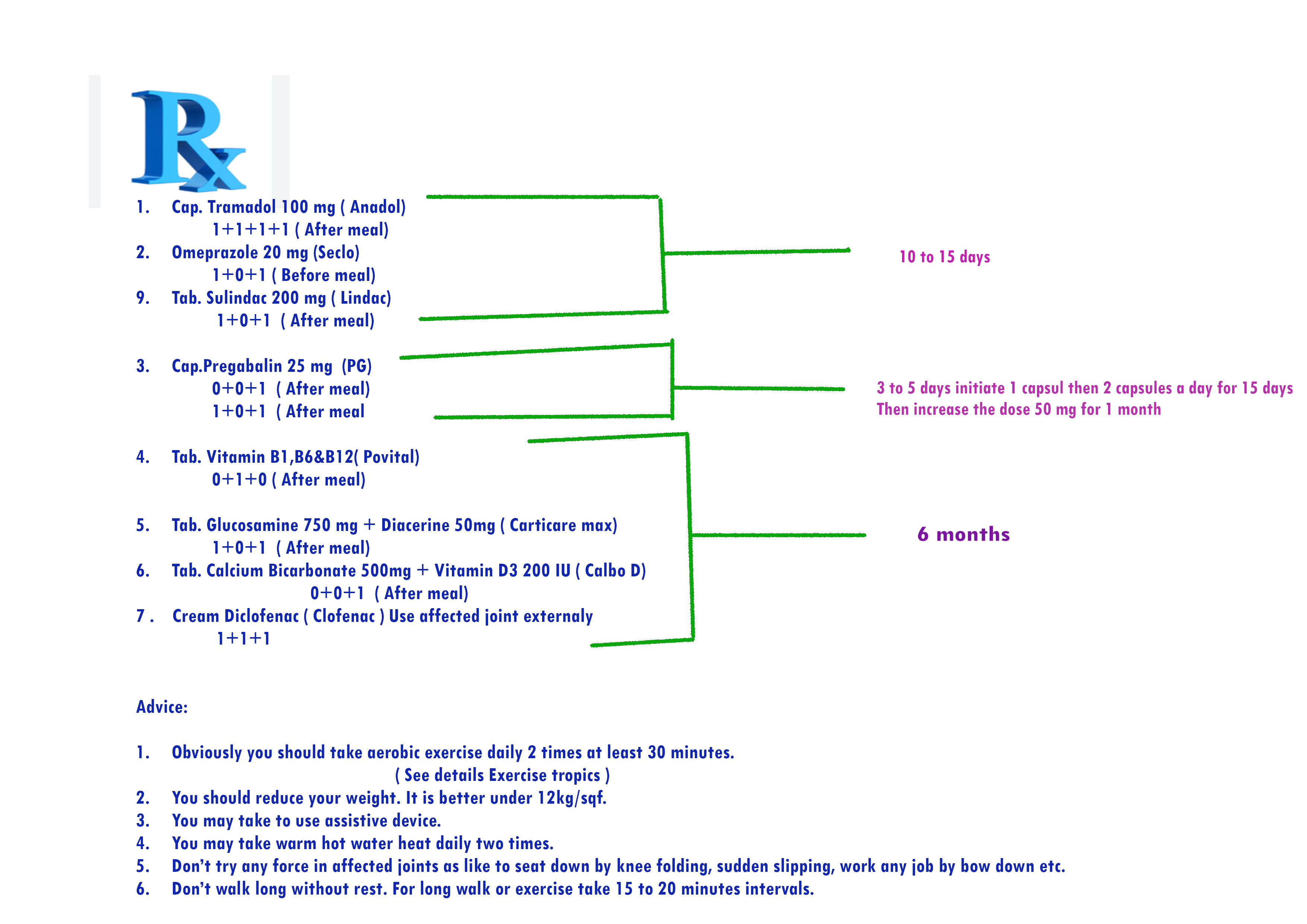
Prescription No.7 for mild and acute osteoarthritis patient who have acute kidney disease
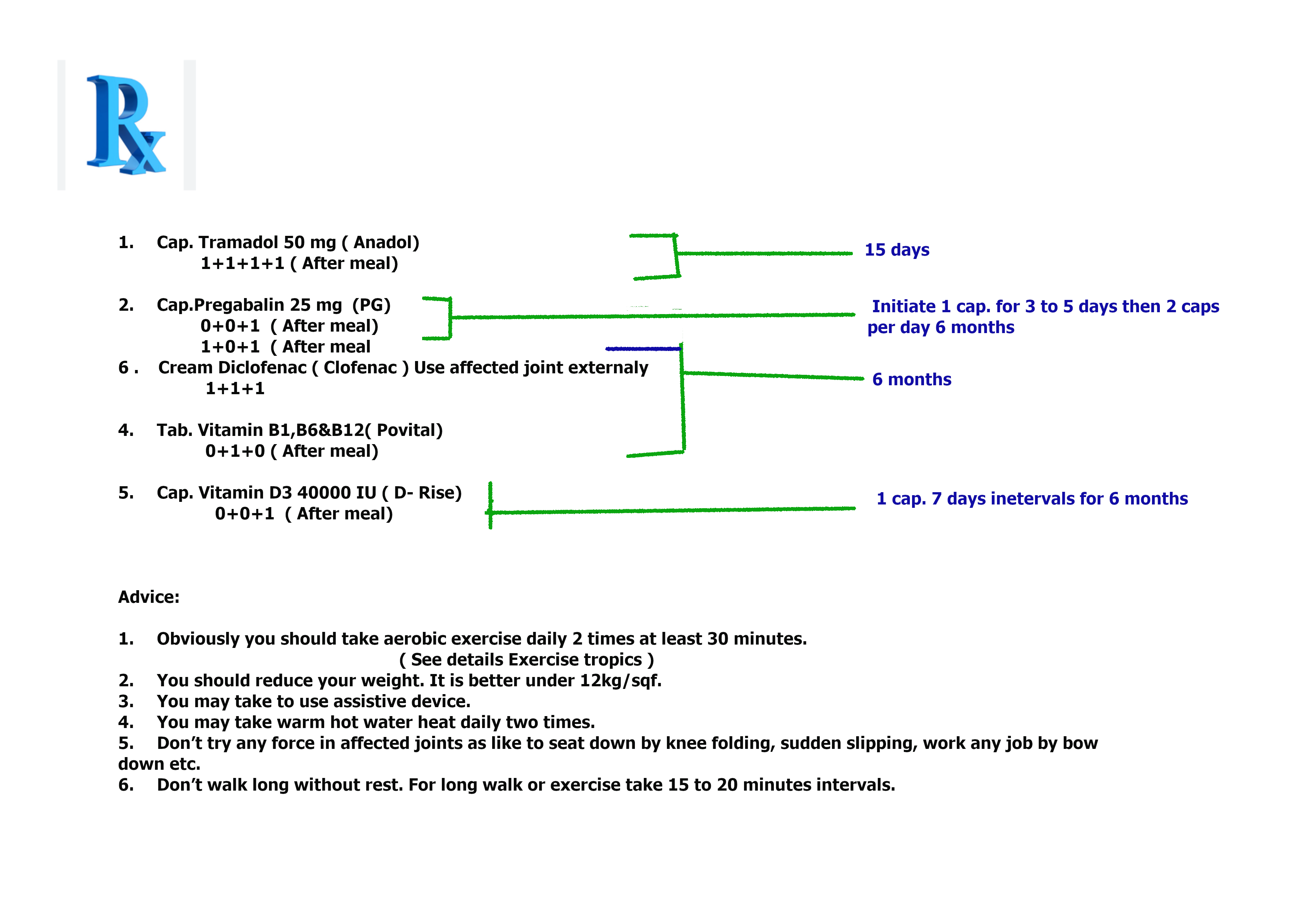
Prescription No.8 for mild osteoarthritis patient who have peptic or gastric ulcer and blood coagulation disorder
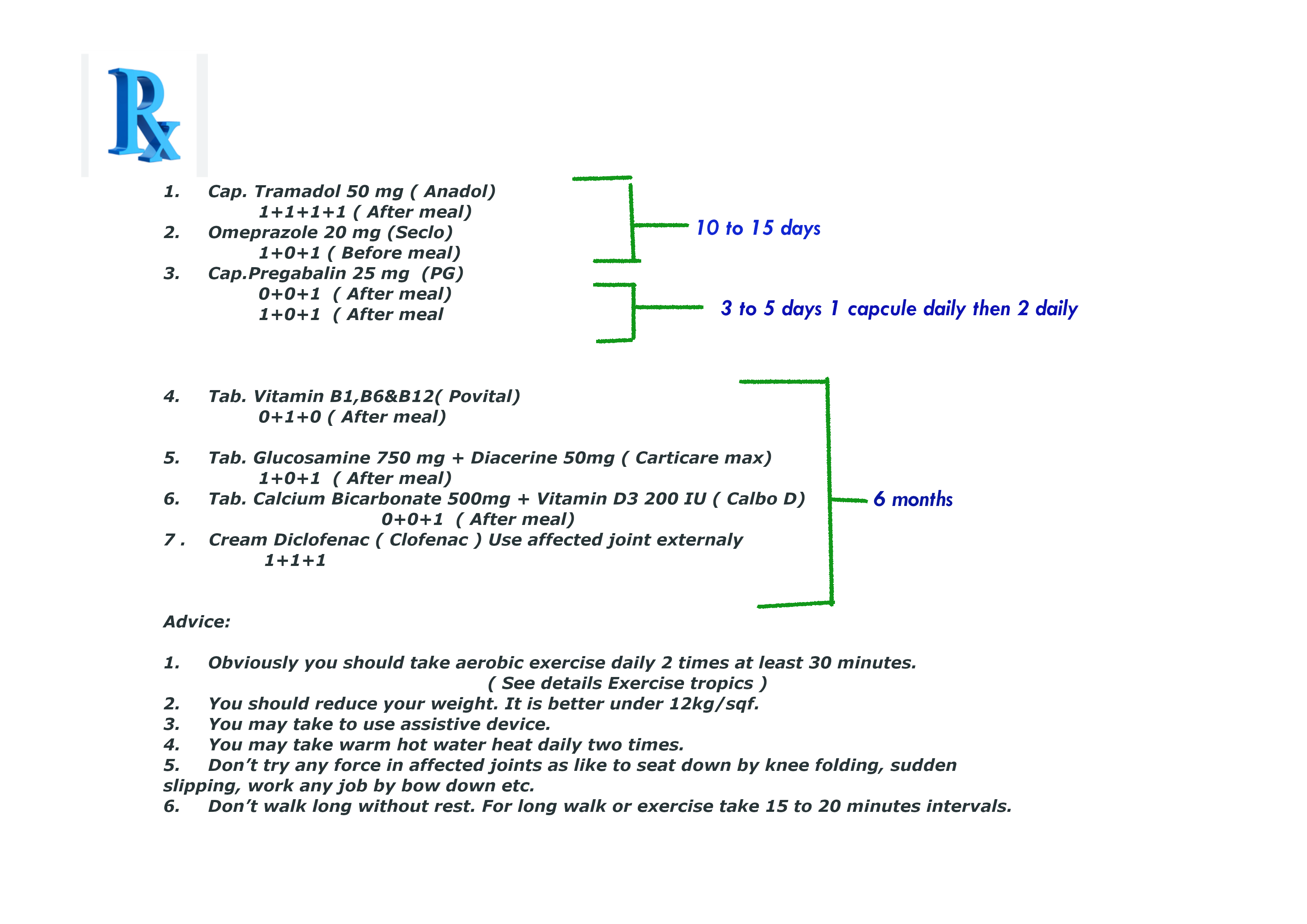
Prescription No.9 for acute osteoarthritis patient who have peptic or gastric ulcer and blood coagulation disorder
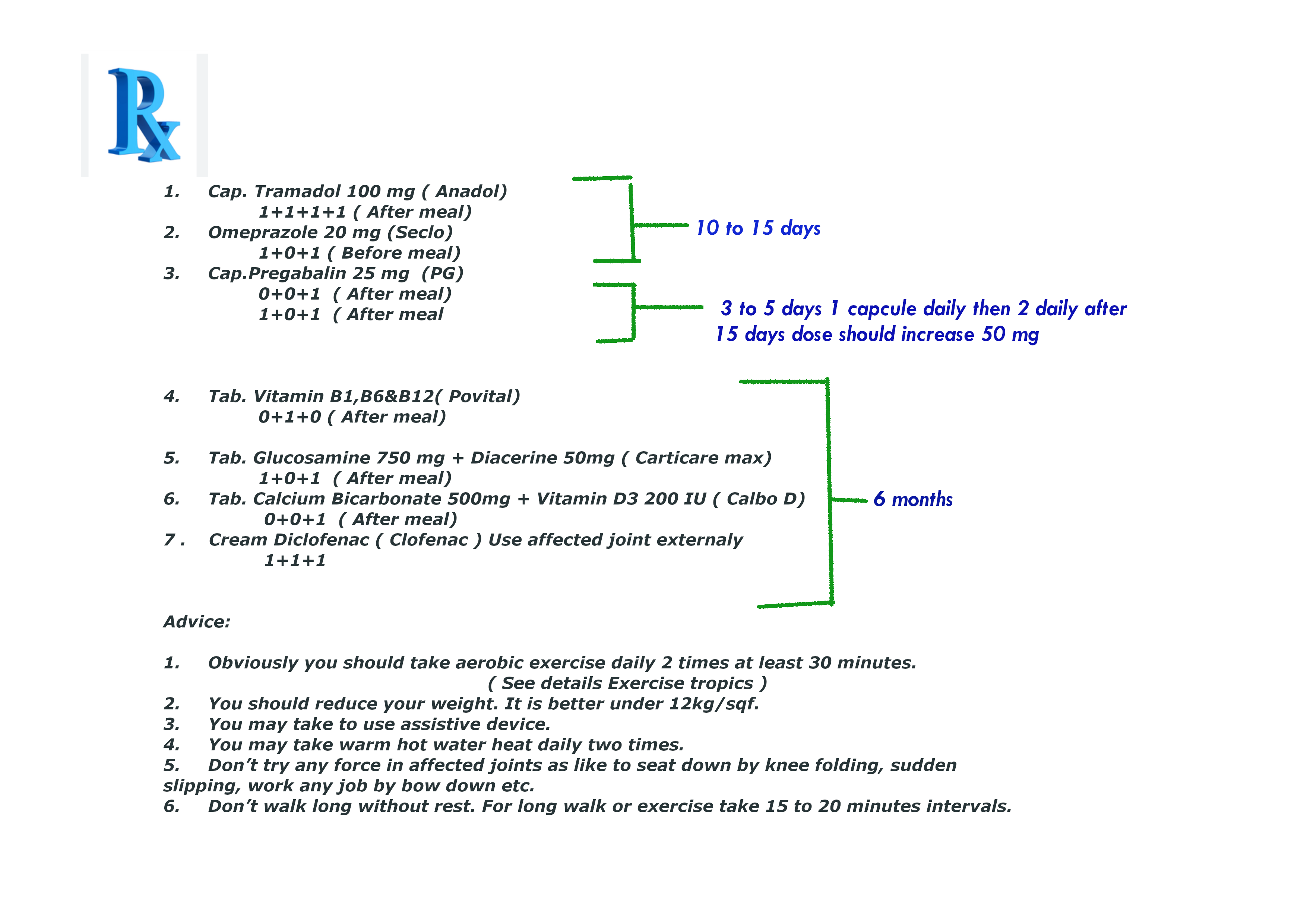
Note : Prescription No 4, 5,6,7,8 & 9 is not contraindicated for diabetics patient but little conscious for liver cirrhosis patients.
-
Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs ( DMARDs)
It is a first line therapy for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis disease. Long time therapy more than eight months for getting effective results and withdrawal of the medicine. This therapy needs highly monitoring about the result of drug effects.
I suggest avoiding this medication for its lots of side effects and critical monitoring effects. If any patient is under a physician with strict monitoring only that patient can take these medicines.
It needs a combination therapy with two DMARDs or other DMARDs with anotherNSAIDs.
3.1. (DMARDs with others DMARDs)
[ 8 months to 2 years ]
3.1.1 Methotrexate
Dose : 7.5 to 25 mg once weekly .
With
3.1.2.. Sulfasalazine
Dose : 500 mg to 3g daily.
Side effects
Most side effects are
- GI disturbance
- Myelosuppression
- Hepatotoxicity
- Pneumonitis
- Infections.
-
Biological therapies
These drugs are used after failing DMARDs drugs. Chief class of drugs target TNF- Alpha, interleukins-1, interleukin-6 that are cytokinins mediated activate T- cell release.
4.1. Infliximab
Dose: 3 mg/kg at weeks for 0,2 and 6 weeks then 8 weeks thereafter.
Administration rout : Intravenous (IV).
OR
4.2. Adalimumab
Dose: 40 mg every two weeks
Side effects
– Lymphoma
– Infection any organ
– Immunosuppressed
– Heart failure
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common inflammatory disorders with not only the joint but a wide range of extra articular organs. Early treatment is not possible and will lead to progressive joint deformity and increase morbidity and mortality. It increased co- morbidity and mortality include infection renal impairment cardiovascular disease and lymphomas.
Etiology and pathophysiology
-Hormonal factor
– Genetic factor
– Environmental factors
– Cigarette smoking
-Infiltrate a variety of inflammatory cells into the joints.
Clinical manifestation
Disease onset is usually insidious with the predominant symptoms being pain, stiffness and swelling.
Affected area are
– The metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints of the fingers.
-Interphalangeal joints of the thumbs.
-The warts
-Metatarsophalangeal joints of the toes.
-Joints of upper and lower Limbs such as the elbows, shoulders and knees.
-Myalgia, fatigue, low grade fever, weight loss.
Diagnosis
Rheumatoid arthritis diagnose made based on
– Patient history
– Presenting symptoms
– Clinical finding
– Ultrasound for the presence of synovitis and X-rays
– Later demonstrate joint destruction
American rheumatism Association made a criteria for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Morning stiffness in and around the joints for at last 6 weeks lasting at least 1 hour before maximal improvement.
- Swelling of 3 or more joints for at least 6 weeks
- Swelling of the wrist, metacarpophalangeal or Proximal interphalangeal joints For at least 6 weeks.
- Symmetric joint swelling for at least 6 weeks.
- Hard X rays changes typical of rheumatoid arthritis that must include erosion or unequivocal bony decalcification around the joints.
- Rheumatoid subcutaneous nodules.
- Positive Rheumatoid factor
The presence of at least 4 of these indicator a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment
Goals is the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- Symptoms relief including pain control
- Slowing or prevention of joint damage
- Preserving and improving functional ability
- Achieving and maintaining disease remission
Rheumatoid arthritis need two types of treatment simultaneously like osteoarthritis
- Non pharmacological treatment
- pharmacological treatment
Non pharmacological treatment
Non pharmacological treatment are most important for the rheumatoid arthritis patients.
It may does by
-Patient education ( tips on joint protection and exercise program)
-Weight loss
– Aerobic exercise program to increase muscle strength
– Physical therapy
– Use assistive device
– Acupuncture may reduce the pain
– Thermal therapy
Pharmacological treatment
Initially patient are treated by DMARDs combination with other glucocorticoids, NSAIDs or simple analgesic.
1.Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs ( DMARDs)
It is a first line therapy for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis disease. Long time therapy more than eight months for getting effective results and withdrawal of the medicine. This therapy needs highly monitoring about the result of drug effects.
I suggest avoiding this medication for its lots of side effects and critical monitoring effects. If any patient is under a physician with strict monitoring only that patient can take these medicines.
It needs a combination therapy with two DMARDs or other DMARDs with anotherNSAIDs.
1.1. (DMARDs with others DMARDs)
[ 8 months to 2 years ]
1.1.1 Methotrexate
Dose : 7.5 to 25 mg once weekly .
With
1.1.2.. Sulfasalazine
Dose : 500 mg to 3g daily.
2.1. (DMARDs with others NSAIDs or SAIDs)
2.1.1 Methotrexate
Dose : 7.5 to 25 mg once weekly .
With
2.1.2. Diclofenac
Dose : 50 mg twice dayily for 15 days
or
2.1.3. Prednisolone
Dose: 5 mg twice daily for 15 days.
Side effects
Most side effects are
- GI disturbance
- Myelosuppression
- Hepatotoxicity
- Pneumonitis
- Infections.
Other medication like analgesic, steroid or biological agent are used same as like as osteoarthritis treatment.
Pharmacological treatment by medication are similar like osteoarthritis.
Prescription N0 1 & 2. for mild rheumatoid arthritis :
Who don’t follow the prescription No. 1 ( Contraindication )-
Patient are suffering by post morbidity or mortality disease like
- Chronic kidney disease
- Chronic liver cirrhosis
- Chronic infected patient
- Hematological disorder
Prescription N0 1 for mild rheumatoid arthritis.
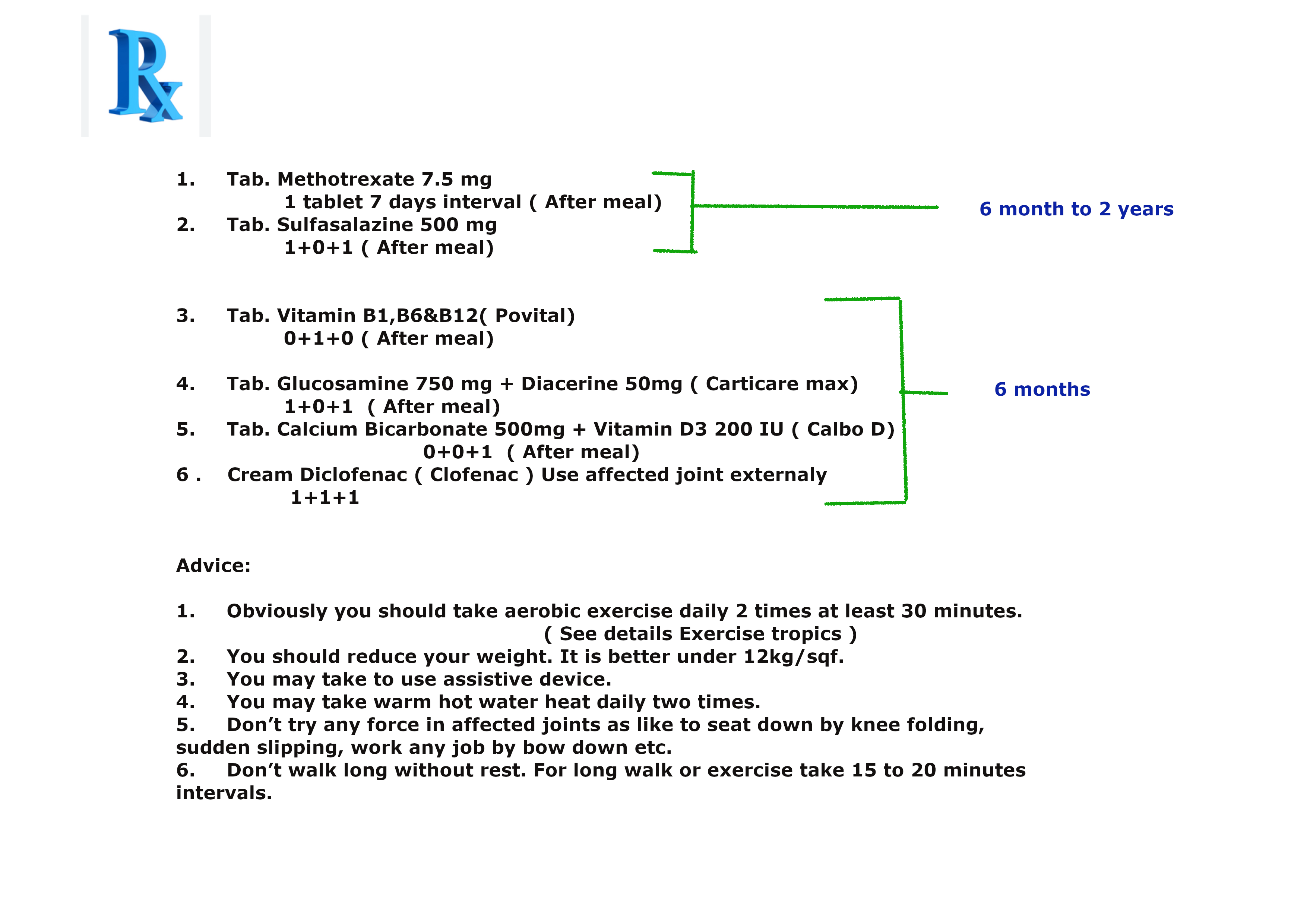
Or
Prescription N0 2 for mild rheumatoid arthritis.
Who don’t follow the prescription No. 2 & 3 ( Contraindication )-
Patient are suffering by post morbidity or mortality disease like
- Chronic kidney disease
- Chronic liver cirrhosis
- Peptic or Gastric ulcer patient and any other coagulation disorder patients like hemophilia.
- Heart failure patient
- Chronic infected patient
- Hematological disorder
- Chronic diabetics patient
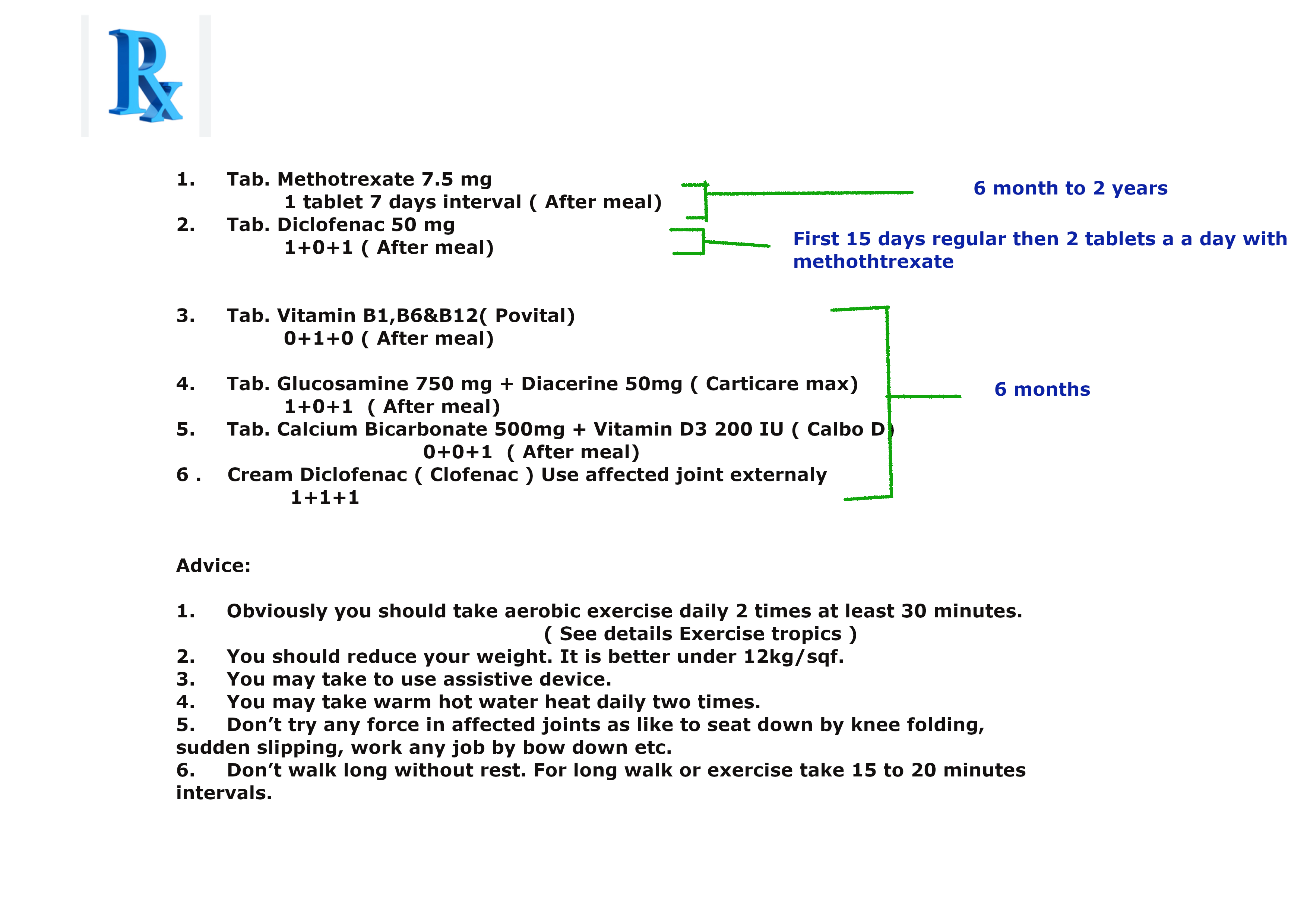
Or
Prescription N0 3 for mild rheumatoid arthritis.
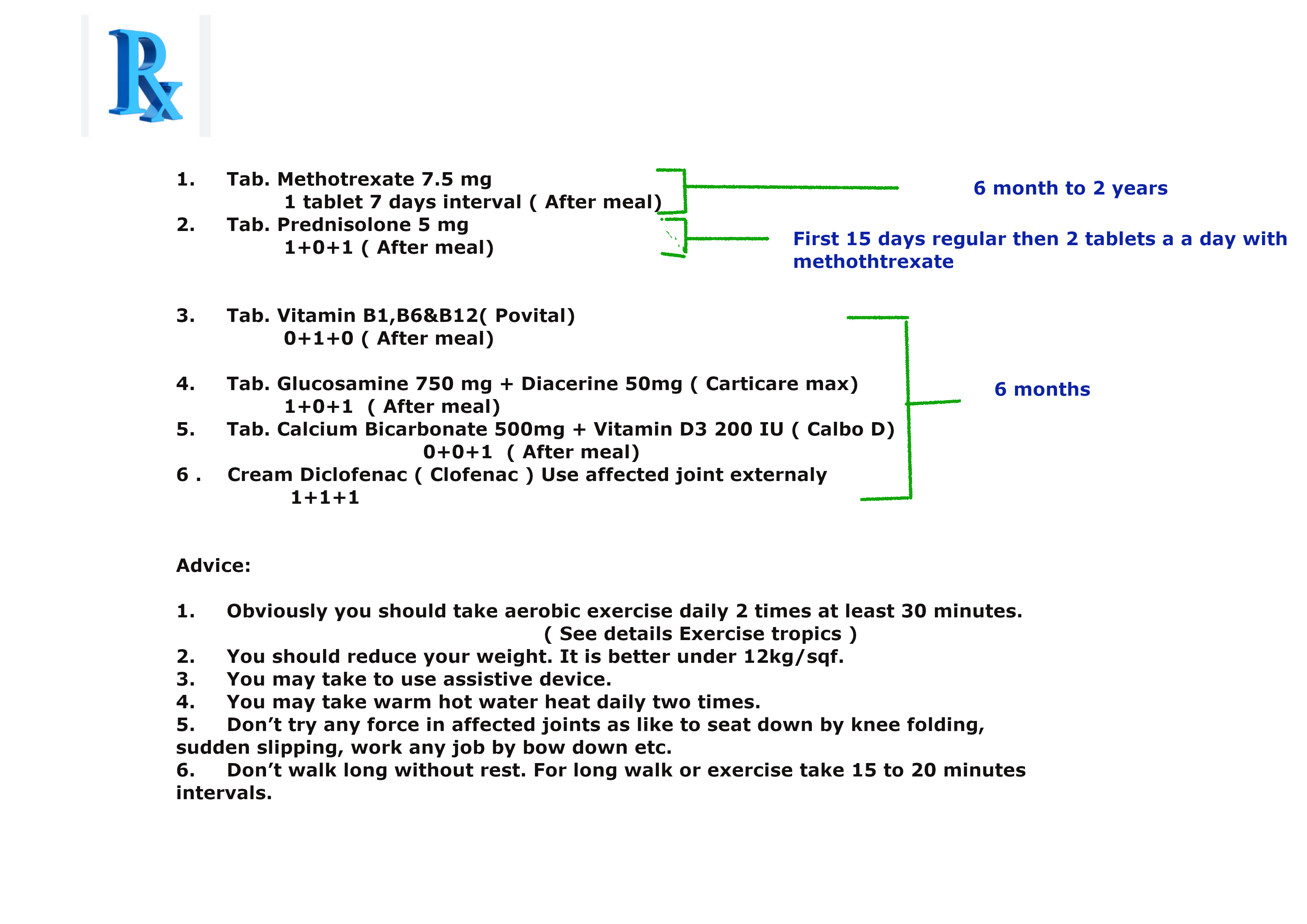
Prescription N0 4 & 5. for mild osteoarthritis :
Who don’t follow the prescription No. 4,5 & 6 ( Contraindication )-
Patient are suffering by post morbidity or mortality disease like
- Chronic diabetics
- Chronic kidney disease
- Chronic liver cirrhosis
- Peptic or Gastric ulcer patient and any other coagulation disorder patients like hemophilia.
- Heart failure patient
Prescription N0 4 for mild rheumatoid arthritis..

Prescription N0 5. rheumatoid arthritis.:

Prescription N0 6. for acute rheumatoid arthritis:

Prescription for rheumatoid arthritis patient who have specific co- morbidity or mortality disease
Prescription No 7. for acute rheumatoid arthritis. patient who also a peptic or gastric ulcer patient

Who don’t follow the prescription No. 7 ( Contraindication )-
Patient are suffering by post morbidity or mortality disease like
- Chronic kidney disease
- Any other coagulation disorder patients like hemophilia.
Prescription No. 8 for mild rheumatoid arthritis patient who have also a mild kidney disease-

Prescription No 9. for Acute rheumatoid arthritis patient who have mild kidney disease

Prescription No. 10 for mild and acute rheumatoid arthritis patient who have acute kidney disease:

Prescription No.11 for mild rheumatoid arthritis patient who have peptic or gastric ulcer and blood coagulation disorder:

Prescription No.12 for acute rheumatoid arthritis patient who have peptic or gastric ulcer and blood coagulation disorder

Note : Prescription No 7, 8,9,10,11 & 12 is not contraindicated for diabetics patient but little conscious for liver cirrhosis patients.
Supplementary can be co-administrate
4.1. Glucosamine sulfate
Dose: 7500 mg 2 times a day
4.2 . Diacerein
Dose: 50 mg 2 times a day
5.1. calcium carbonate
Dose: 500 mg once daily
5.2. Vitamin D3
Dose: 200 IU once a day
