Hyperuricemia and Gout
Hyperuricemia
Hyperuricemia indicate increase the serum uric acid level.It means more than 7 mgl uric acid in serum.
Gout
Gout is a disease characterized by recurrent painful acute attack of urate crystals that may induce arthritis. It may include tophi in and around joint.
Pathophysiology
Cause
Hyperuricemia and gout are two types
- Primary hyperuricemia and gout are resulted by
- Uric acid over production
- Impaired renal clearance of uric acid or a combination of their ( Uric acid over production depends on some enzymatic defects eg. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT), phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate(PRPP). )
Access uric acid level > 800 mg to 1 gram daily.
- Secondary hyperuricemia and gout are resulted by
- Hematological causes (eg. Lymphoproliferative disorder, Myeloproliferative disorder, Certain hemolytic anemia and hemoglobinopathies.)
- Chronic renal failure
- Drugs (eg. aspirin, diuretics except spironolactone, Cyclosporin, Ethambutol, Nicotinic acid, Fenofibrate, Losartan, Vitamin C etc. )
- Ethanol consumption
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Psoriasis
- Chronic lead poisoning
Risk factors
- Genetics ( eg. A Polymorphism of the SLC22A12 gene Which encodes for URAT-1 Responsible uric acid secretion, Polymorphism of the SLC2A9 gene Responsible for Glucose and Fructose transporter GLU9. )
- Renal disease
- Co- Morbidities (eg. Obesity, dyslipidemia, Glucose intolerance, Hypertension, diabetics).
- Diet ( eg. high purine contain food like mea ).
- Alcohol consumption
- Medication
Clinical presentation diagnosis and treatment:
Hyperuricemia and gout can divided by several clinical presentation and treatment
There are
-
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia
Clinical presentation
- Deposit of urine in join soft tissue in kidney
- Maximum time join remain symptoms free.
- Some concurrent diseases like cardiovascular disease, diabetics and tension may induce hyperuricemia.
- Serum urate levels of up to 13 mg/dL for men and 10 mg/dL for women .
Treatment
Drugs therapy
Maximum time is not require urate level lowering drugs. Although drugs may use increase urine output that may prevent the Uric acid stone formation.
Medication 1:
- 1.1. Angiotensin- 2- receptor blocker drugs, (eg. Olmesartan Medoxomil).
Example: Olmesartan ( Olmesan)
Dose: 20 mg Daily as single dose for 3 months.
- 1.2. Sulindac ( Lindac)
Dose: 100 mg Twice Daily for 10 days.
- 1.3. AnyH2 receptors blocker drugs or PPI
Example: Famotidine ( Famomax)
Dose: 20 mg Twice Daily for 10 days before meal.
Prescription No. 1 for the asymptomatic hyperuricemia.

Prescription No. 1 for the asymptomatic hyperuricemia ( contraindicated for the patient who are)
- Chronic kidney disease patients
- Chronic liver disease patients
- Chronic peptic or gastric ulcer disease patients
-
Acute gouty arthritis:
Acute gouty arthritis is Characterized by painful arthritic attack of sudden onset. Trauma, exposure to cold dietary overindulgence or another triggering event may be involved in the development of the acute attack.
Signs and symptoms
- The affected joints typically become hot, Swollen and extremely tender.
- The most common site of the initial attack is the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
- Other sides that may be affected include the instep, ankle, heel, knee, Wrist, elbow and fingers.
- Initial attack is abrupt, usually occurring at night or in the early morning.
- Untreated first attack in War 3 to 14 days partially or completely joint pain and information.
- Edema subsides, local desquamation and pruritus may occur.
- Symptoms during on acute attack may include fever, chills and malaise.
Diagnostic criteria
- Elevated serum uric acid level
- Elevated serum Leukocytosis and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Treatment goals
- Relieve pain and inflammation
- Terminate the acute attack
- Restore normal function to the affected joints
- Increase immobilization of the affected joints
Therapy
Medication
The acute gouty arthritis medication need to steps –
Step 1:
At first step acute attack should need to control by using antiinflammatory drugs therapy for 1 to 2 weeks.
Medication for step 1
2.1. Sulindac ( eg. Limdac)
Dose: 200 mg twice daily after meal for 15 days
2.2. Any H2 receptor blocker or any PPI drugs .
Example: Famotidine(eg. Famomax)
Dose: 20 mg twice daily before meal for 15 days.
Medication for step 2
2.3. Febuxostat (eg. Febustat)
Dose: 40 mg once daily after meal for 6 months.
If serum uric acid level not reduce less than 6 mg/dl dose should increased-
Dose would be: 80 mg once daily after a meal for 1.5 months then dose can balance 40 mg
once daily after meal for 6 months.
2.4. Indomethacin ( Indomet)
Dose: 50 mg three times daily after meal for 15 days.
2.5. Any H2 receptor blocker or any PPI drugs .
Example: Famotidine(eg. Famomax)
Dose: 20 mg twice daily before meal for 15 days.
Contraindication of this medicine
- Severe gastric or peptic ulcer patient
- severe kidney patient
- chronic liver disease
Monitoring
- patient should monitor liver function test and sign and symptoms of myocardial infarction and stock.
Some direct prescription are given bellow that you can apply according to your body condition.
Prescription No. 2 for the acute gouty arthritis

Contraindication of this medicine(Prescription No. 2 for the acute gouty arthritis)
- Severe gastric or peptic ulcer patient
- Severe kidney patient
- Chronic liver disease
- Chronic diabetics patients
Prescription No. 3 for the acute gouty arthritis
For the patients who also affected co-morbidity disease like
- Mild kidney patients
- Diabetics patient
- Mild gastric or peptic ulcer disease
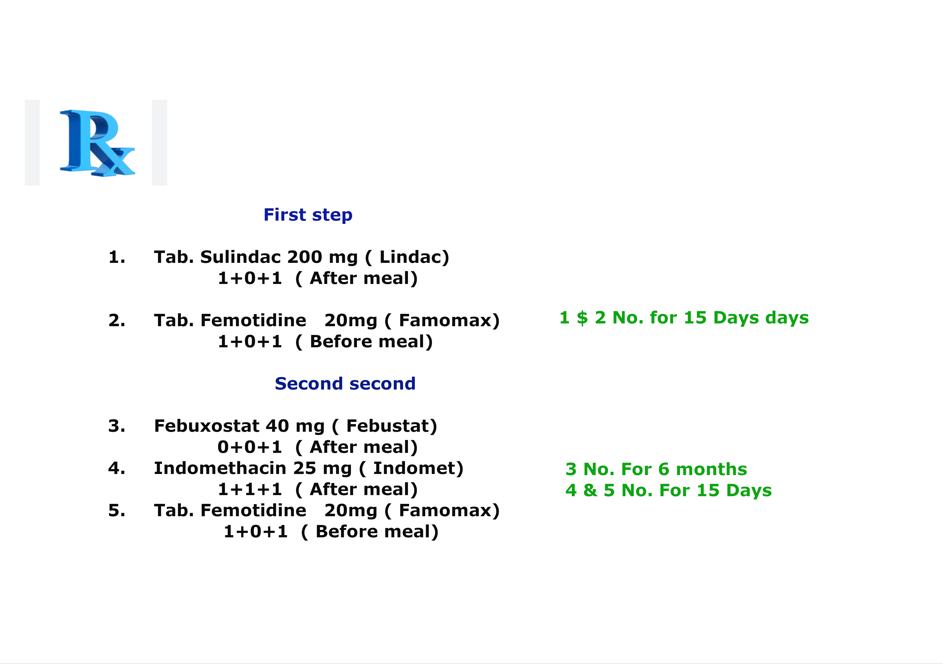
Contraindication of this medicine(Prescription No. 3 for the acute gouty arthritis)
- Severe gastric or peptic ulcer patient
- Severe kidney patient
- Severe liver disease
Prescription No. 4 for the acute gouty arthritis
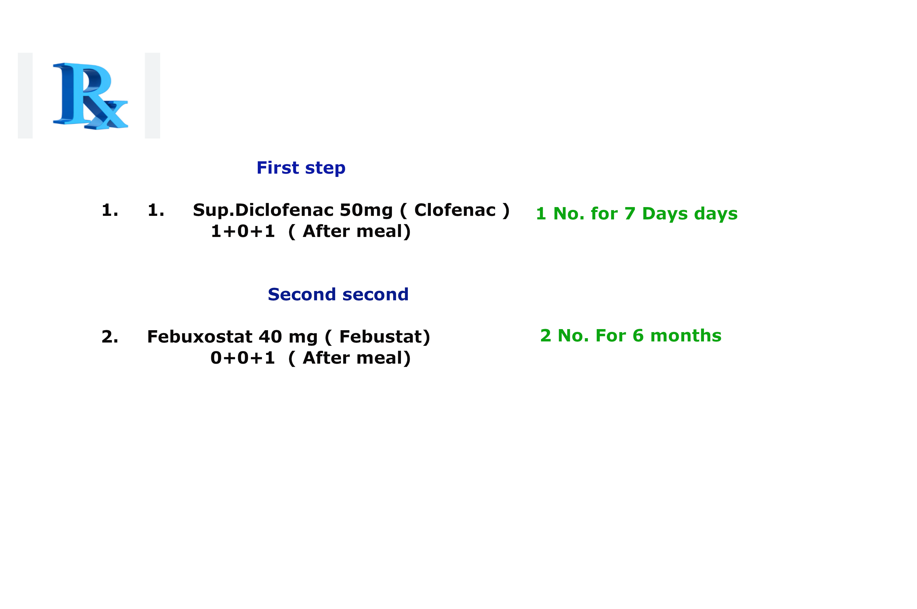
Prescription No. 4 for the acute gouty arthritis
For the patients who also affected co-morbidity disease like
- Mild kidney patients
- Diabetics patient
- Sever gastric or peptic ulcer disease
Contraindication of this medicine(Prescription No. 4 for the acute gouty arthritis)
- Severe kidney patient
- Severe liver disease
-
Intercritical gout
Intercritical gout may be interrupted by the recurrence of acute attack. In untreated patients the second attack occurs within 2 years of the first, some patients delayed for 5 to 10 years.
- If patients aren’t treated, become progressively longer and more severe and may involve more than one joint.
- Tophi forms one or more joints.
Treatment goals
- Reduce the frequency and security of recurrent attack.
- Minimize urad deposition in body tissue their by preventing progressive to chronic tophaceous gout.
- Target uric acid level below less than <5 mg/dl.
Medication
Medication for intercritical gout are similar like Acute gouty arthritis.
The intercritical gout medication need to steps –
Step 1:
At first step acute attack should need to control by using ant inflammatory drugs therapy for 1 to 2 weeks.
Medication for step 1
2.1. Sulindac ( eg. Limdac)
Dose: 200 mg twice daily after meal for 15 days
2.2. Any H2 receptor blocker or any PPI drugs .
Example: Famotidine(eg. Famomax)
Dose: 20 mg twice daily before meal for 15 days.
Medication for step 2
2.3. Febuxostat (eg. Febustat)
Dose: 40 mg once daily after meal for 6 months.
If serum uric acid level not reduce less than 6 mg/dl dose should increased-
Dose would be: 80 mg once daily after a meal for 1.5 months then dose can balance 40 mg
once daily after meal for 6 months.
2.4. Indomethacin ( Indomet)
Dose: 50 mg three times daily after meal for 15 days.
2.5. Any H2 receptor blocker or any PPI drugs .
Example: Famotidine(eg. Famomax)
Dose: 20 mg twice daily before meal for 15 days.
Contraindication of this medicine
- Severe gastric or peptic ulcer patient
- severe kidney patient
- chronic liver disease
Monitoring
- patient should monitor liver function test and sign and symptoms of myocardial infarction and stock.
Some direct prescription are given bellow that you can apply according to your body condition.
Prescription No. 5 for the Intercritical gout

If serum uric acid level not reduce less than 6 mg/dl dose should increased- Should follow Prescription No. 6
Prescription No. 6 for the Intercritical gout

Contraindication of this medicine(Prescription No.5 & 6 for the acute gouty arthritis)
- Severe gastric or peptic ulcer patient
- Severe kidney patient
- Chronic liver disease
- Chronic diabetics patients
Prescription No. 7 for the Intercritical gout
For the patients who also affected co-morbidity disease like
- Mild kidney patients
- Diabetics patient
- Mild gastric or peptic ulcer disease

Contraindication of this medicine(Prescription No. 7 for the Intercritical gout)
- Severe gastric or peptic ulcer patient
- Severe kidney patient
- Chronic liver disease
Prescription No. 8 for the Intercritical gout

Prescription No. 8 for the Intercritical gout
For the patients who also affected co-morbidity disease like
- Mild kidney patients
- Diabetics patient
- Sever gastric or peptic ulcer disease
Contraindication of this medicine(Prescription No. 8 for the Intercritical gout)
- Severe kidney patient
- Chronic liver disease
-
Chronic tophaceous gout
Long time untreated hyperuricemia and gout may development chronic tophaceous gout and it is rare.
Signs and symptoms
- Tophi in the synovia and one or more joints, soft tissues, subcutaneous tissue.
- Destroy articular cartilage
- joint deformities.
- bone erosions
- Renal disease
- Tophi in the pinna of the external ear.
Treatment
In severe case medications are Combined used
4.1. Allopurinol ( Purinol)
Dose: 100 mg daily as a single dose for one week then 100 mg twice daily.
4.2. Probenecid
Dose: 250 mg daily as a single dose for one week then increase the dose as 500 mg once daily.
Prescription No. 9 for the Chronic tophaceous gout

Advice to the patients
- overweight patients must reduce weight gradually ( Careful not Rapid reduction).
- Diet should strictly maintain, IT should balance diet which ratio of calories source of total diet is carbohydrate 40%, protein 30% and unsaturated fat 30% of total energy.
- Avoid purine and purine-containing diets.
- should avoid alcohol consumption.
- should avoid contraindicating medication like Aspirin, losartan, cyclosporine, Vitamin C, fenofibrate etc.
- Patients should take at least 2 L water when taking uricosuric agents.
- Daily two times should take free hand exercise at least 40 minutes.
