use-Rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and treatment.
Rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and treatment??
What is rheumatoid arthritis ??
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and eventually leading to joint damage if left untreated. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is caused by wear and tear on the joints, RA occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium—the lining of the membranes that surround the joints.Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common inflammatory disorders with not only the joint but a wide range of extra articular organs. Early treatment is not possible and will lead to progressive joint deformity and increase morbidity and mortality. It increased co- morbidity and mortality include infection renal impairment cardiovascular disease and lymphomas.
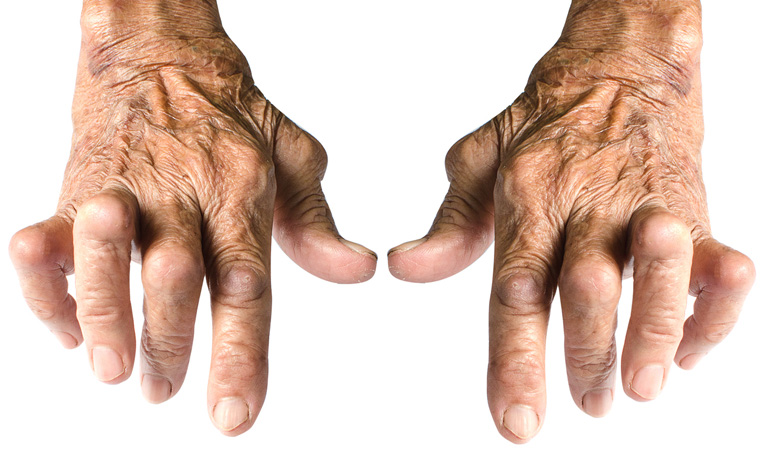
Etiology and pathophysiology
-Hormonal factor
– Genetic factor
– Environmental factors
– Cigarette smoking
-Infiltrate a variety of inflammatory cells into the joints.
Clinical manifestation
Disease onset is usually insidious with the predominant symptoms being pain, stiffness and swelling.
Affected area are
– The metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints of the fingers.
-Interphalangeal joints of the thumbs.
-The warts
-Metatarsophalangeal joints of the toes.
-Joints of upper and lower Limbs such as the elbows, shoulders and knees.
-Myalgia, fatigue, low grade fever, weight loss.
Symptoms
- Joint pain and stiffness: Typically affects smaller joints first (e.g., fingers and toes) and can spread to larger joints over time.
- Swelling: Inflamed joints can become swollen, warm, and tender to the touch.
- Fatigue: Many people with RA experience persistent fatigue and a general feeling of being unwell.
- Morning stiffness: Stiffness that lasts for more than 30 minutes after waking up is common.
- Symmetry: RA often affects joints symmetrically (e.g., both wrists or both knees).
Causes
The exact cause of RA is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors, such as infections or smoking, which may trigger the immune system to attack the joints.
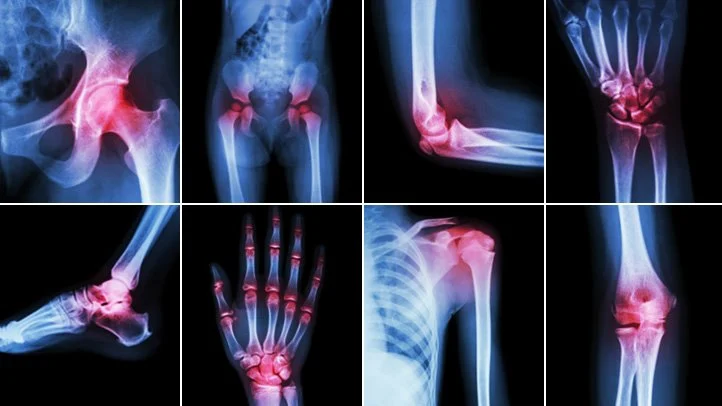
Diagnosis
RA is diagnosed based on symptoms, physical exams, blood tests, and imaging studies. Blood tests often look for rheumatoid factor (RF) or anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies, which are commonly found in people with RA. Imaging, such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs, can help assess the extent of joint damage.
Need proper diagnosis
Rheumatoid arthritis diagnose made based on
– Patient history
– Presenting symptoms
– Clinical finding
– Ultrasound for the presence of synovitis and X-rays
– Later demonstrate joint destruction
American rheumatism Association made a criteria for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Morning stiffness in and around the joints for at last 6 weeks lasting at least 1 hour before maximal improvement.
- Swelling of 3 or more joints for at least 6 weeks
- Swelling of the wrist, metacarpophalangeal or Proximal interphalangeal joints For at least 6 weeks.
- Symmetric joint swelling for at least 6 weeks.
- Hard X rays changes typical of rheumatoid arthritis that must include erosion or unequivocal bony decalcification around the joints.
- Rheumatoid subcutaneous nodules.
- Positive Rheumatoid factor
The presence of at least 4 of these indicator a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment
There is no cure for RA, but various treatments can manage symptoms and slow disease progression:
- Medications: These include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents that target specific parts of the immune system.
- Physical therapy: Helps maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength.
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and quitting smoking can help manage symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be needed to repair or replace damaged joints.
Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment are key to managing RA effectively and preventing long-term joint damage.
Prevention
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reduces stress on joints, particularly weight-bearing ones.
- Exercise Regularly: Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling help maintain joint function and muscle strength.
- Avoid Joint Injuries: Protecting joints during physical activities can lower the risk of OA.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially calcium and vitamin D, supports bone health.
Rheumatoid arthritis can significantly impact daily life, but with proper management and lifestyle adjustments, many people can maintain a good quality of life.
You should follow the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis-
Goals is the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- Symptoms relief including pain control
- Slowing or prevention of joint damage
- Preserving and improving functional ability
- Achieving and maintaining disease remission
Rheumatoid arthritis need two types of treatment simultaneously like osteoarthritis
- Non pharmacological treatment
- pharmacological treatment
Non pharmacological treatment
Non pharmacological treatment are most important for the rheumatoid arthritis patients.
It may does by
-Patient education ( tips on joint protection and exercise program)
-Weight loss
– Aerobic exercise program to increase muscle strength
– Physical therapy
– Use assistive device
– Acupuncture may reduce the pain
– Thermal therapy
Pharmacological treatment
In that section i will discuss the treatment with medicine. It is important and useful as primary and secondary stage with easy acceptable to all.
Initially patient are treated by DMARDs combination with other glucocorticoids, NSAIDs or simple analgesic.
1.Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs ( DMARDs)
It is a first line therapy for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis disease. Long time therapy more than eight months for getting effective results and withdrawal of the medicine. This therapy needs highly monitoring about the result of drug effects.
I suggest avoiding this medication for its lots of side effects and critical monitoring effects. If any patient is under a physician with strict monitoring only that patient can take these medicines.
It needs a combination therapy with two DMARDs or other DMARDs with anotherNSAIDs.
1.1. (DMARDs with others DMARDs)
[ 8 months to 2 years ]
1.1.1 Methotrexate
Dose : 7.5 to 25 mg once weekly .
With
1.1.2.. Sulfasalazine
Dose : 500 mg to 3g daily.
2.1. (DMARDs with others NSAIDs or SAIDs)
2.1.1 Methotrexate
Dose : 7.5 to 25 mg once weekly .
With
2.1.2. Diclofenac
Dose : 50 mg twice dayily for 15 days
or
2.1.3. Prednisolone
Dose: 5 mg twice daily for 15 days.
Side effects
Most side effects are
- GI disturbance
- Myelosuppression
- Hepatotoxicity
- Pneumonitis
- Infections.
Note : I suggested that the Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs ( DMARDs) and Biological therapies if you want to take you should need close monitoring with a specialist otherwise you may avoid these medication.
Other medication like analgesic, steroid or biological agent are used same as like as osteoarthritis treatment.
Pharmacological treatment by medication are similar like osteoarthritis.
Prescription N0 1 & 2. for mild rheumatoid arthritis :
Who don’t follow the prescription No. 1 ( Contraindication )-
Patient are suffering by post morbidity or mortality disease like
- Chronic kidney disease
- Chronic liver cirrhosis
- Chronic infected patient
- Hematological disorder
-
Prescription N0 1 for mild rheumatoid arthritis.
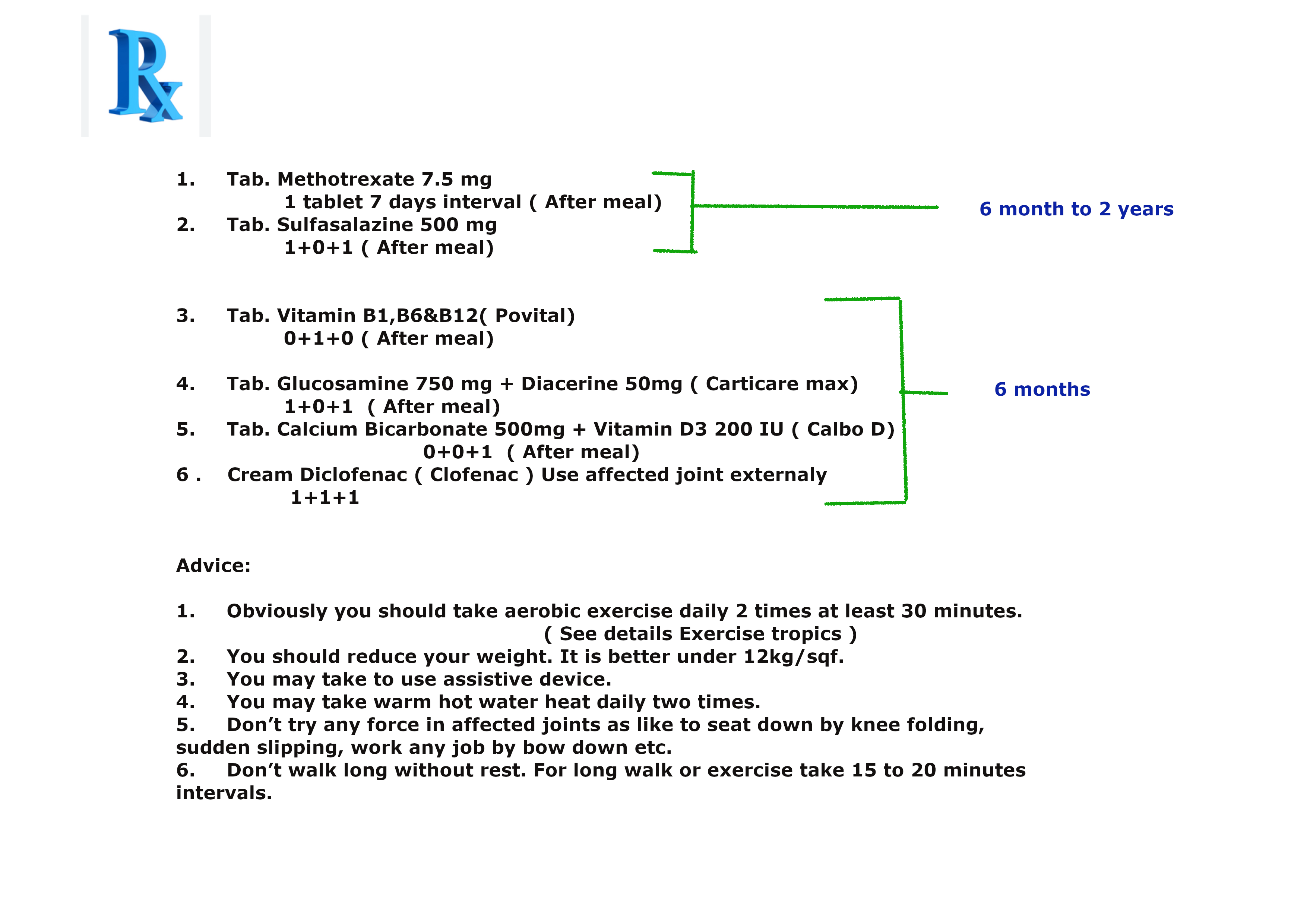
Or
-
Prescription N0 2 for mild rheumatoid arthritis.
Who don’t follow the prescription No. 2 & 3 ( Contraindication )-
Patient are suffering by post morbidity or mortality disease like
- Chronic kidney disease
- Chronic liver cirrhosis
- Peptic or Gastric ulcer patient and any other coagulation disorder patients like hemophilia.
- Heart failure patient
- Chronic infected patient
- Hematological disorder
- Chronic diabetics patient
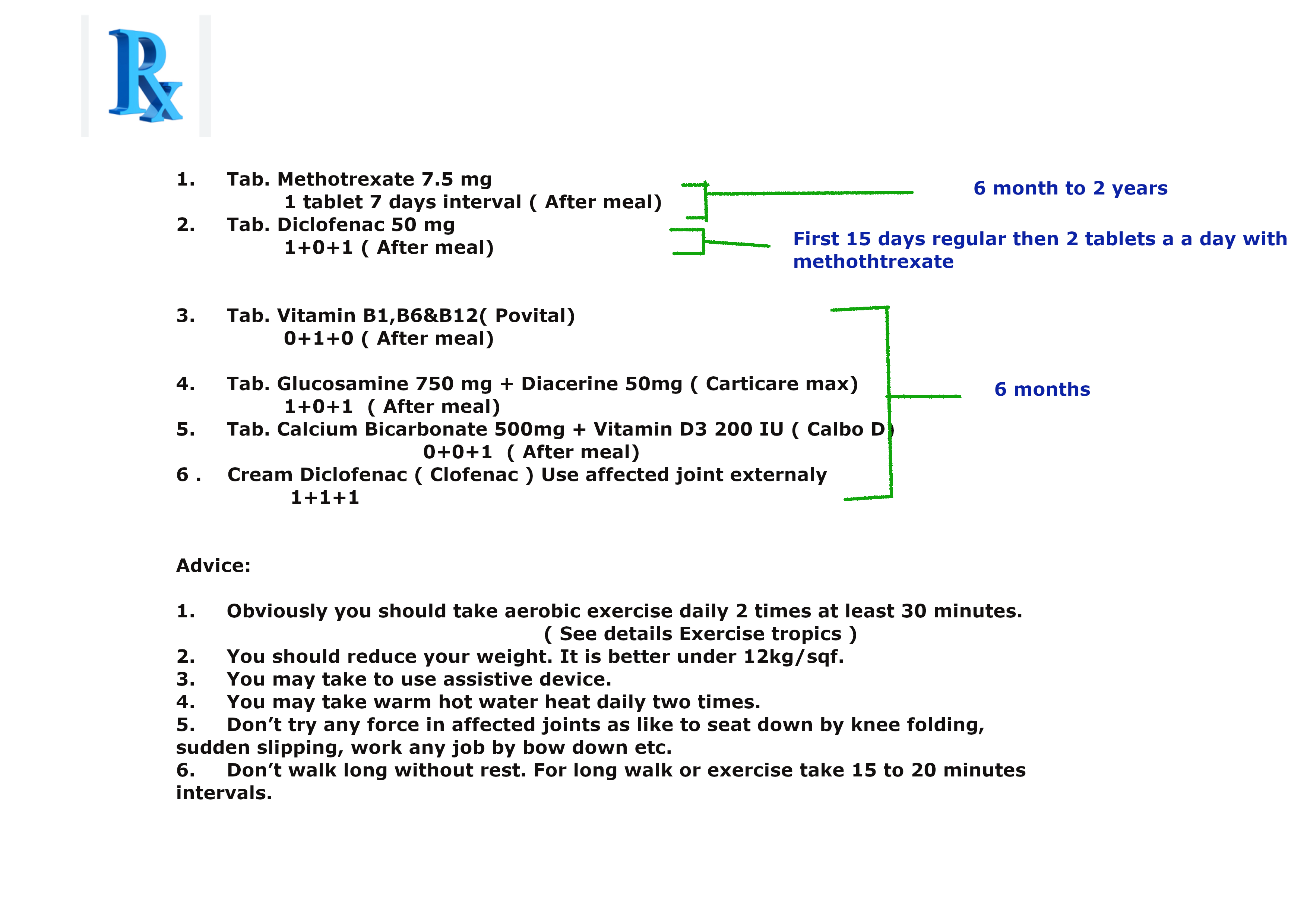
Or
-
Prescription N0 3 for mild rheumatoid arthritis.
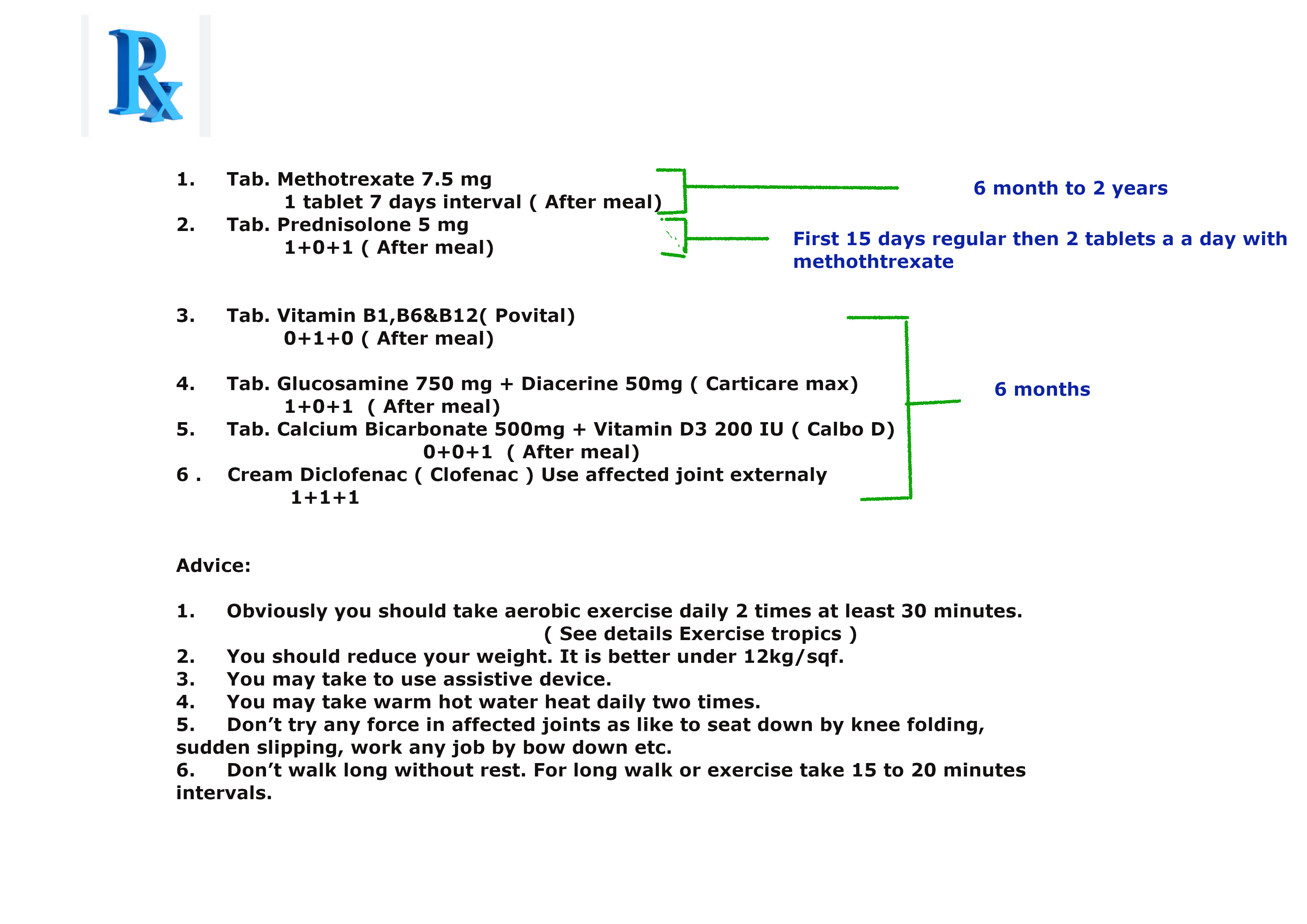
-
Prescription N0 4 & 5. for mild osteoarthritis :
Who don’t follow the prescription No. 4,5 & 6 ( Contraindication )-
Patient are suffering by post morbidity or mortality disease like
- Chronic diabetics
- Chronic kidney disease
- Chronic liver cirrhosis
- Peptic or Gastric ulcer patient and any other coagulation disorder patients like hemophilia.
- Heart failure patient
-
Prescription N0 4 for mild rheumatoid arthritis..

-
Prescription N0 5. rheumatoid arthritis.:
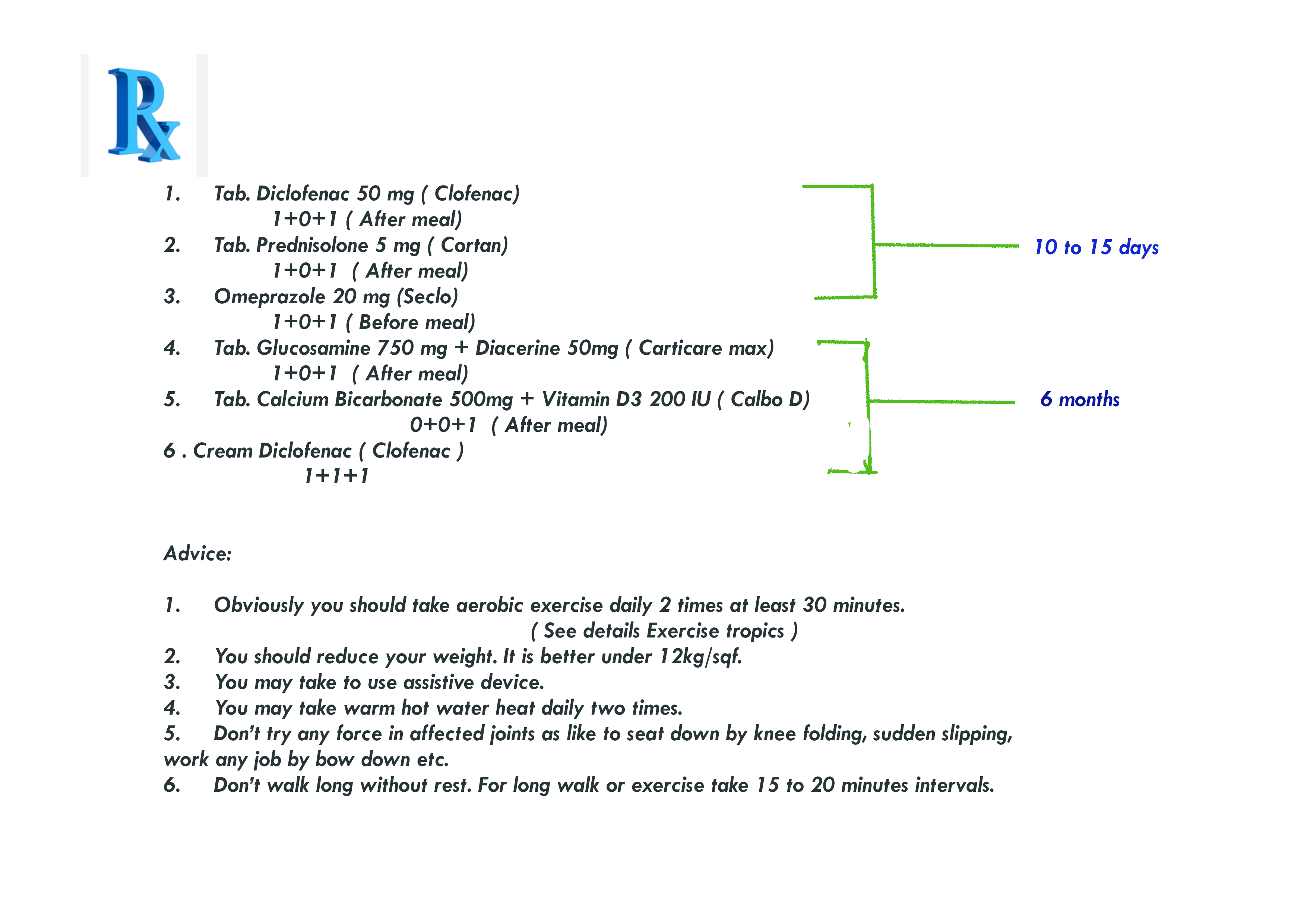
-
Here prescription N0 6. for acute rheumatoid arthritis:
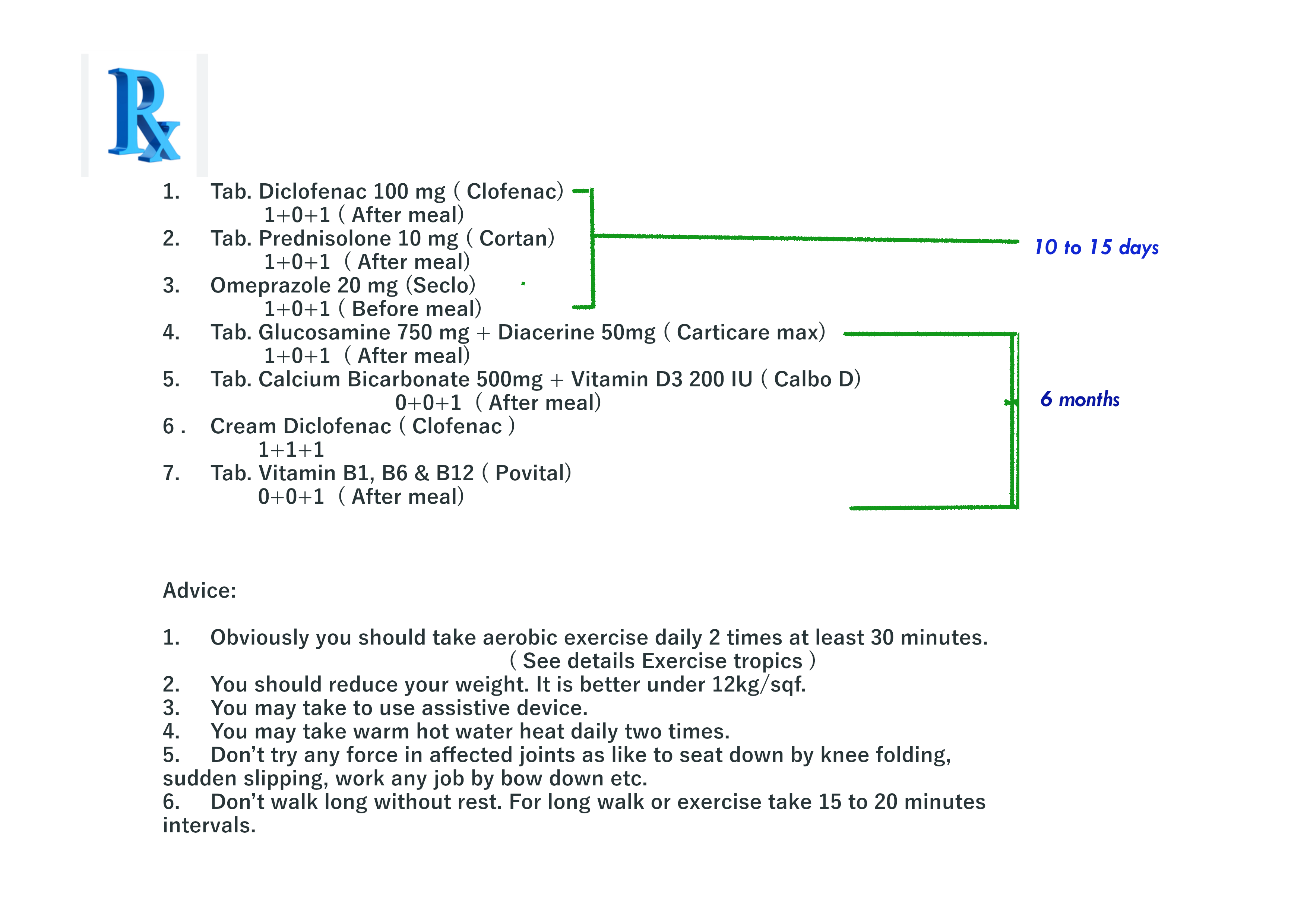
Prescription for rheumatoid arthritis patient who have specific co- morbidity or mortality disease
-
In this situation Prescription No 7. for acute rheumatoid arthritis. patient who also a peptic or gastric ulcer patient
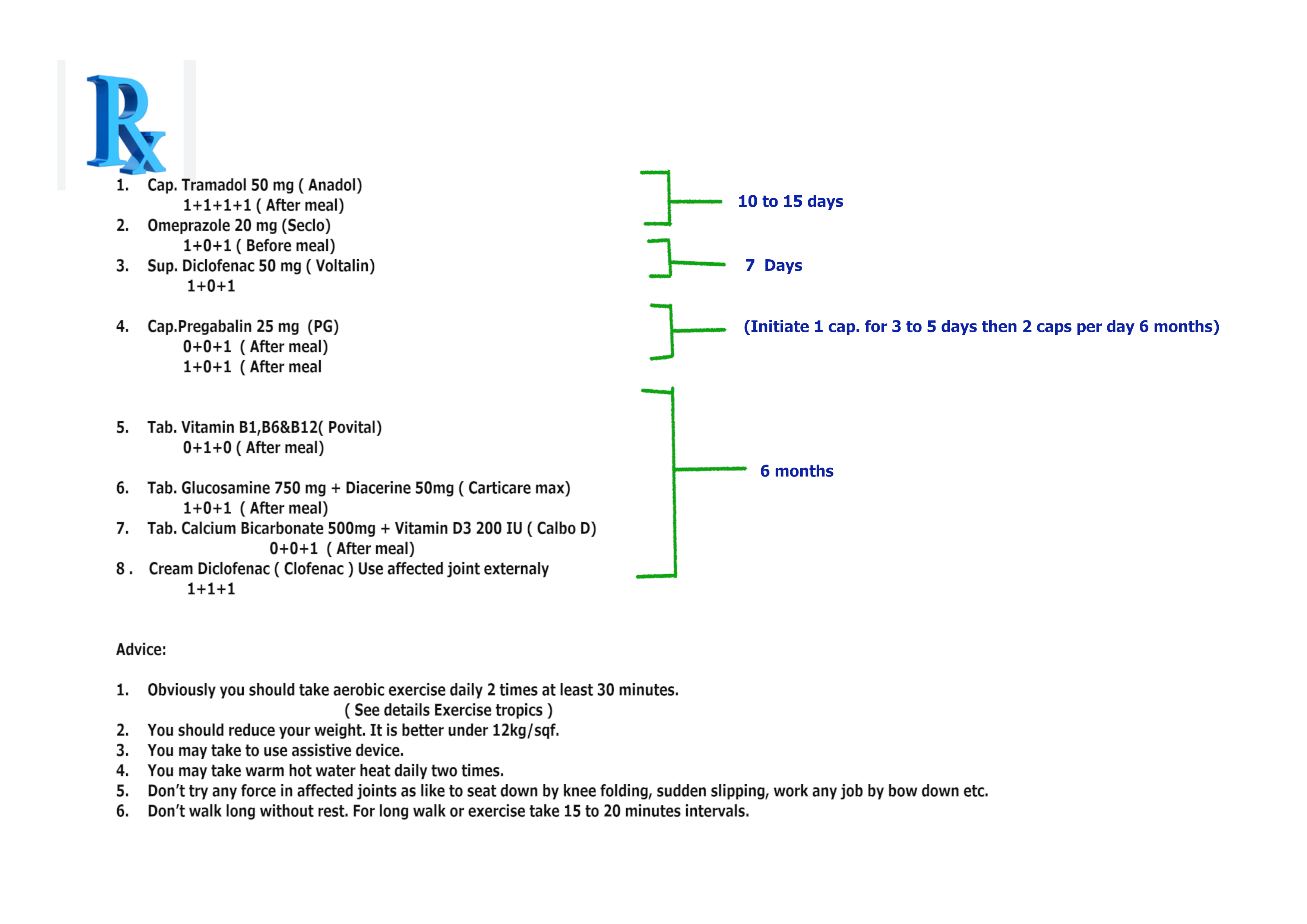
Who don’t follow the prescription No. 7 ( Contraindication )-
Patient are suffering by post morbidity or mortality disease like
- Chronic kidney disease
- Any other coagulation disorder patients like hemophilia.
-
Here prescription No. 8 for mild rheumatoid arthritis patient who have also a mild kidney disease-
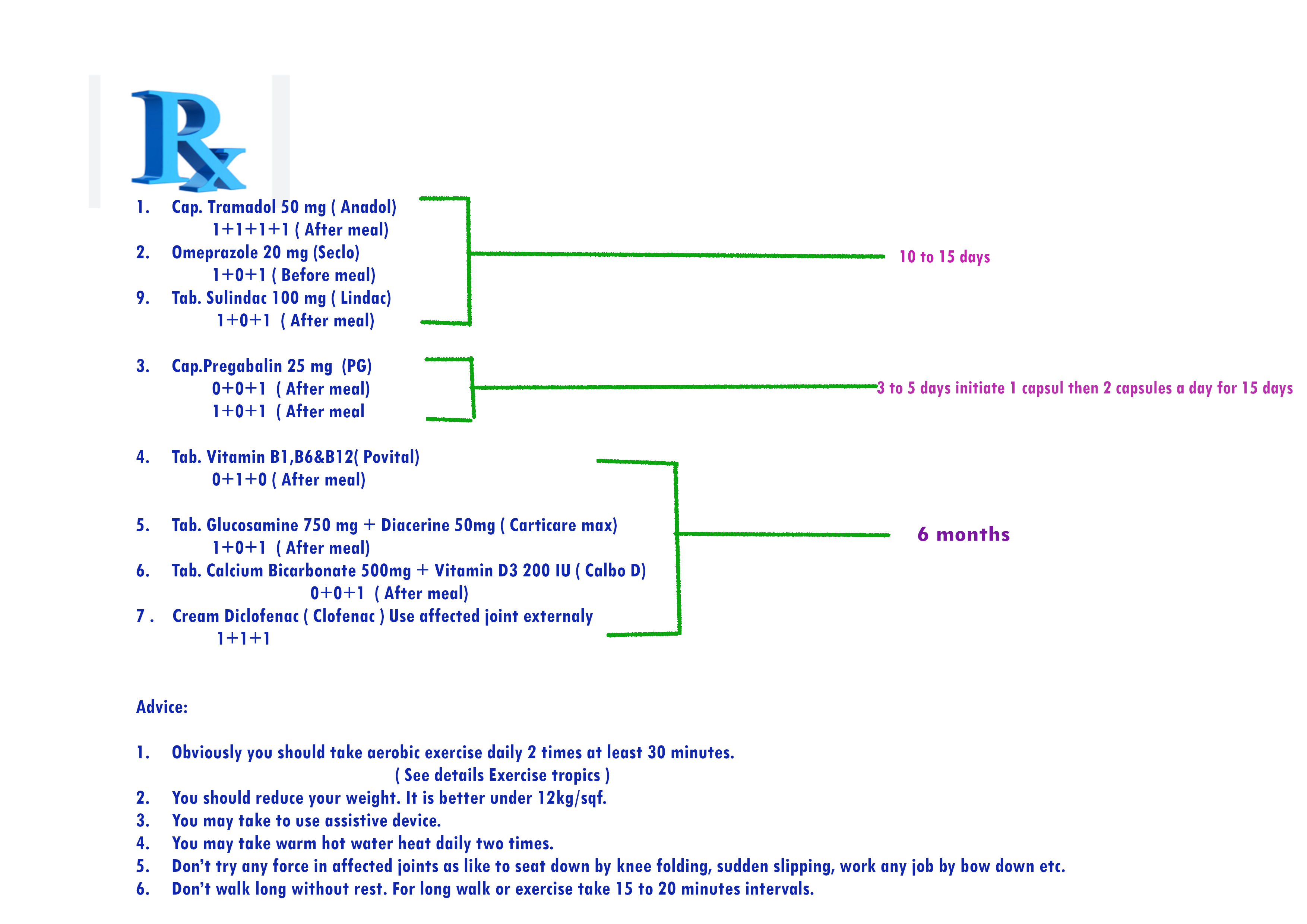
-
Follow the prescription No 9. for Acute rheumatoid arthritis patient who have mild kidney disease
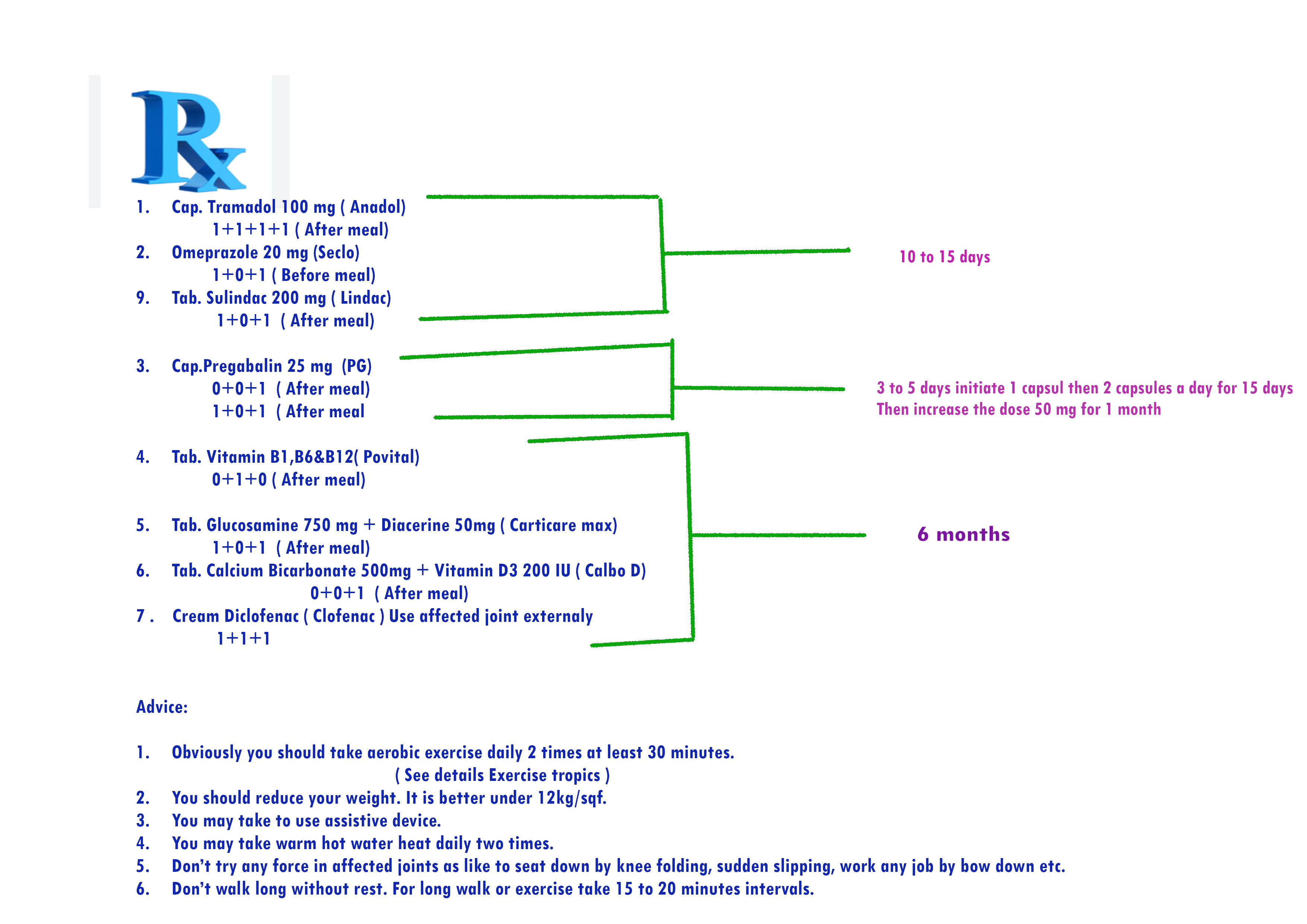
-
Otherwise prescription No. 10 for mild and acute rheumatoid arthritis patient who have acute kidney disease:
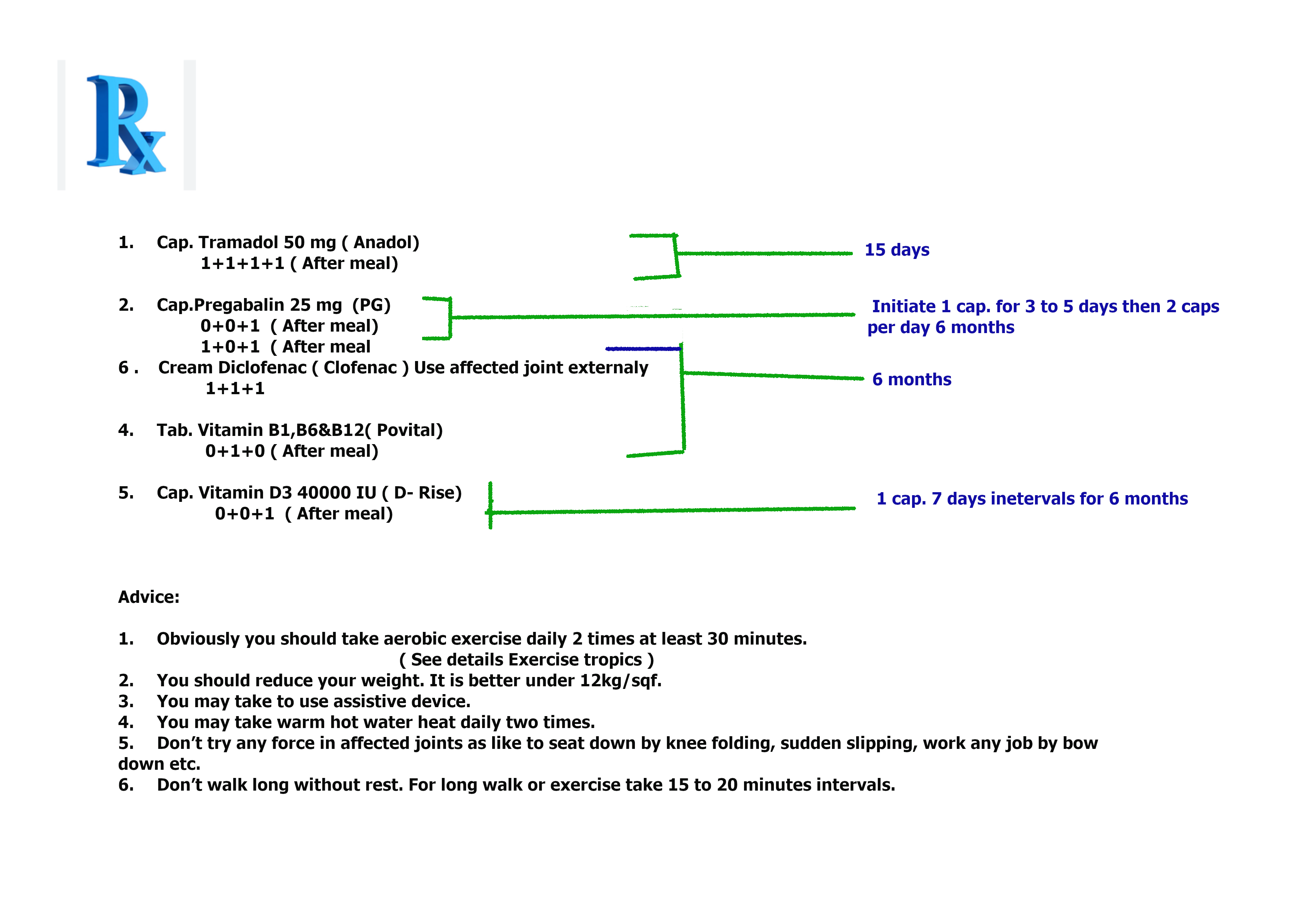
-
Otherhand prescription No.11 for mild rheumatoid arthritis patient who have peptic or gastric ulcer and blood coagulation disorder:
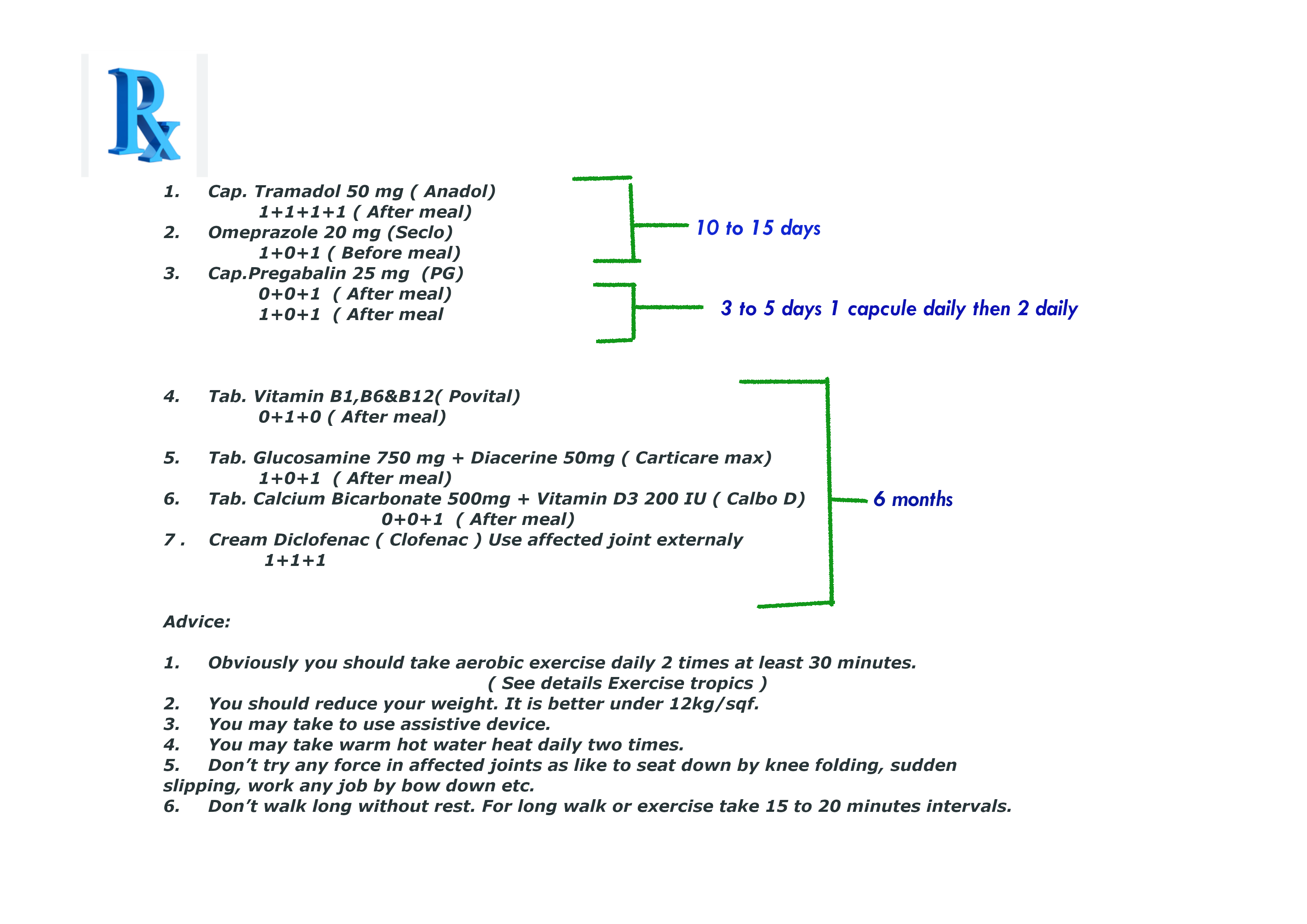
-
Who have peptic or gastric ulcer and blood coagulation disorderPrescription No.12 for acute rheumatoid arthritis patient:
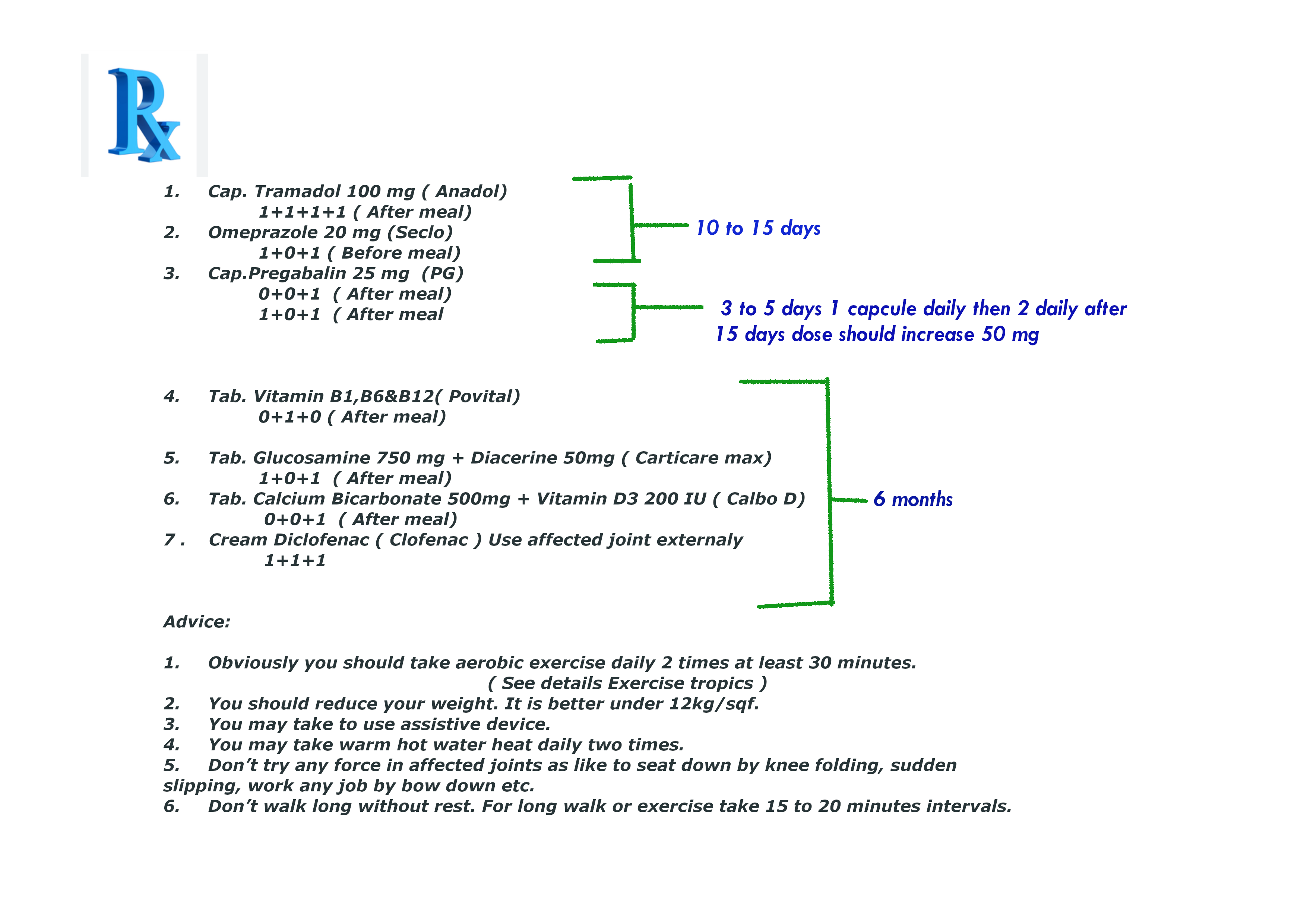
Note : Prescription No 7, 8,9,10,11 & 12 is not contraindicated for diabetics patient but little conscious for liver cirrhosis patients.
Supplementary can be co-administrate with all prescription if you want and have financial support.
Suppliants are given bellow like-
4.1. Glucosamine sulfate
Dose: 7500 mg 2 times a day
4.2 . Diacerein
Dose: 50 mg 2 times a day
5.1. calcium carbonate
Dose: 500 mg once daily
5.2. Vitamin D3
Dose: 200 IU once a day
Prevention of rheumatoid arthritis:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reduces stress on joints, particularly weight-bearing ones.
- Exercise Regularly: Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling help maintain joint function and muscle strength.
- Avoid Joint Injuries: Protecting joints during physical activities can lower the risk of OA.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially calcium and vitamin D, supports bone health.
Rheumatoid arthritis can significantly impact daily life, but with proper management and lifestyle adjustments, many people can maintain a good quality of life.
Note: If you suffer sever rheumatoid arthritis attack and don’t control at home you should go hospital immediately. Tertiary stage of Rheumatoid arthritis is required surgery that might you take.
If anyone want to more information please send to me your question through the given email address.
Email address: mallicktarun@rocketmail.com
For getting treatment base suggestion please contact or request an appointment.
You may also visit you tube video channel that may helpful to you.
